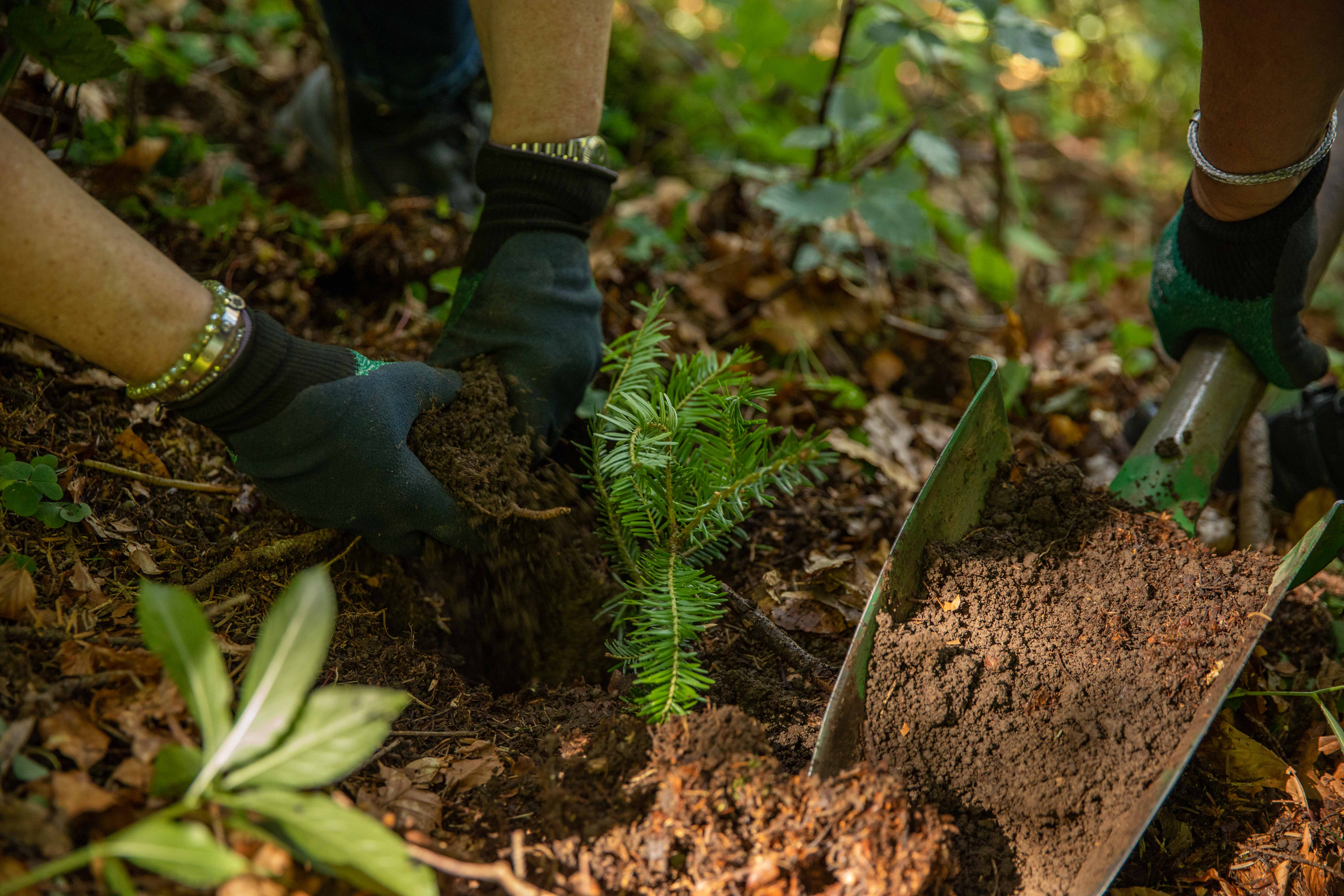
Afforestation for better living conditions in Kikonda, Uganda, China, India
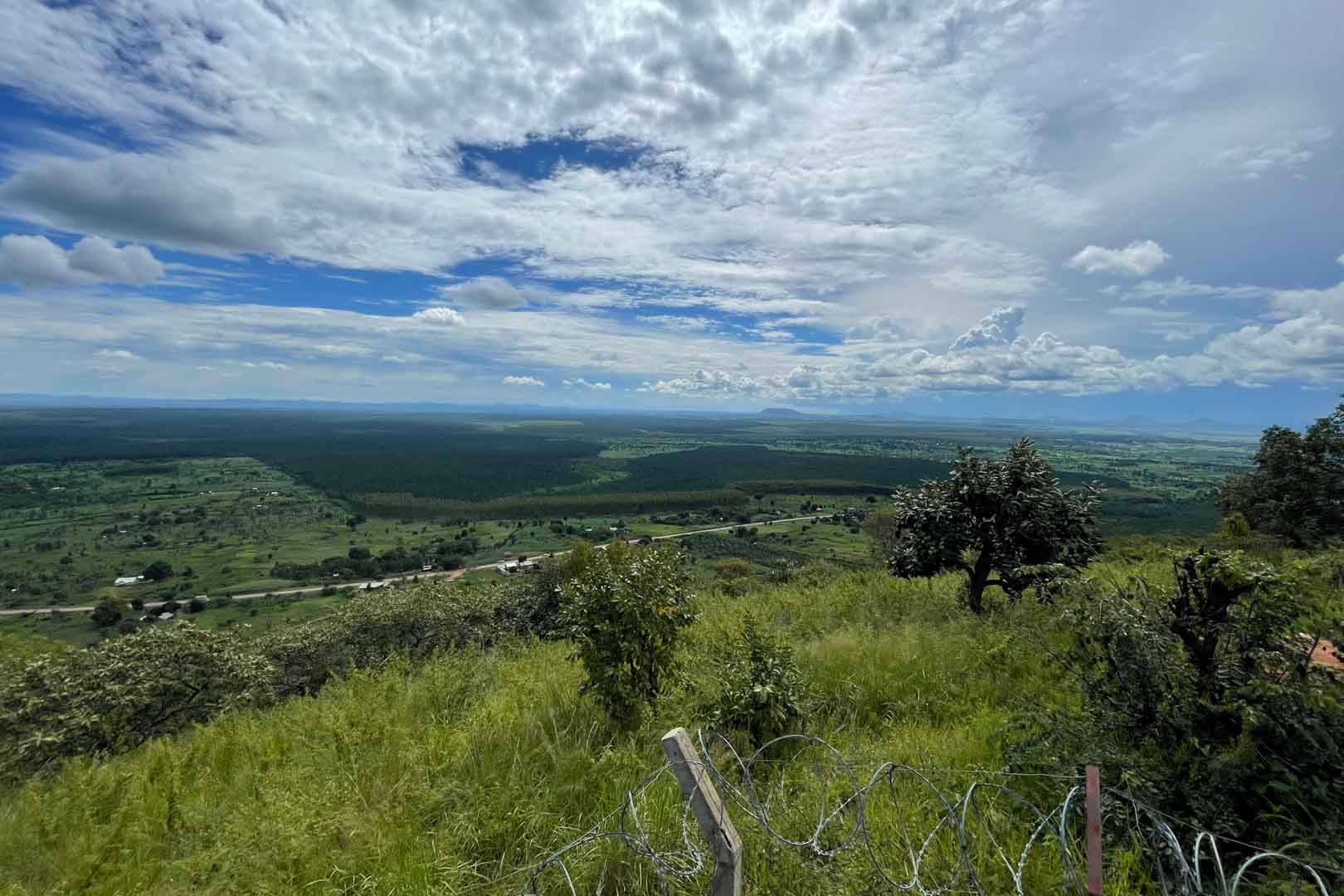
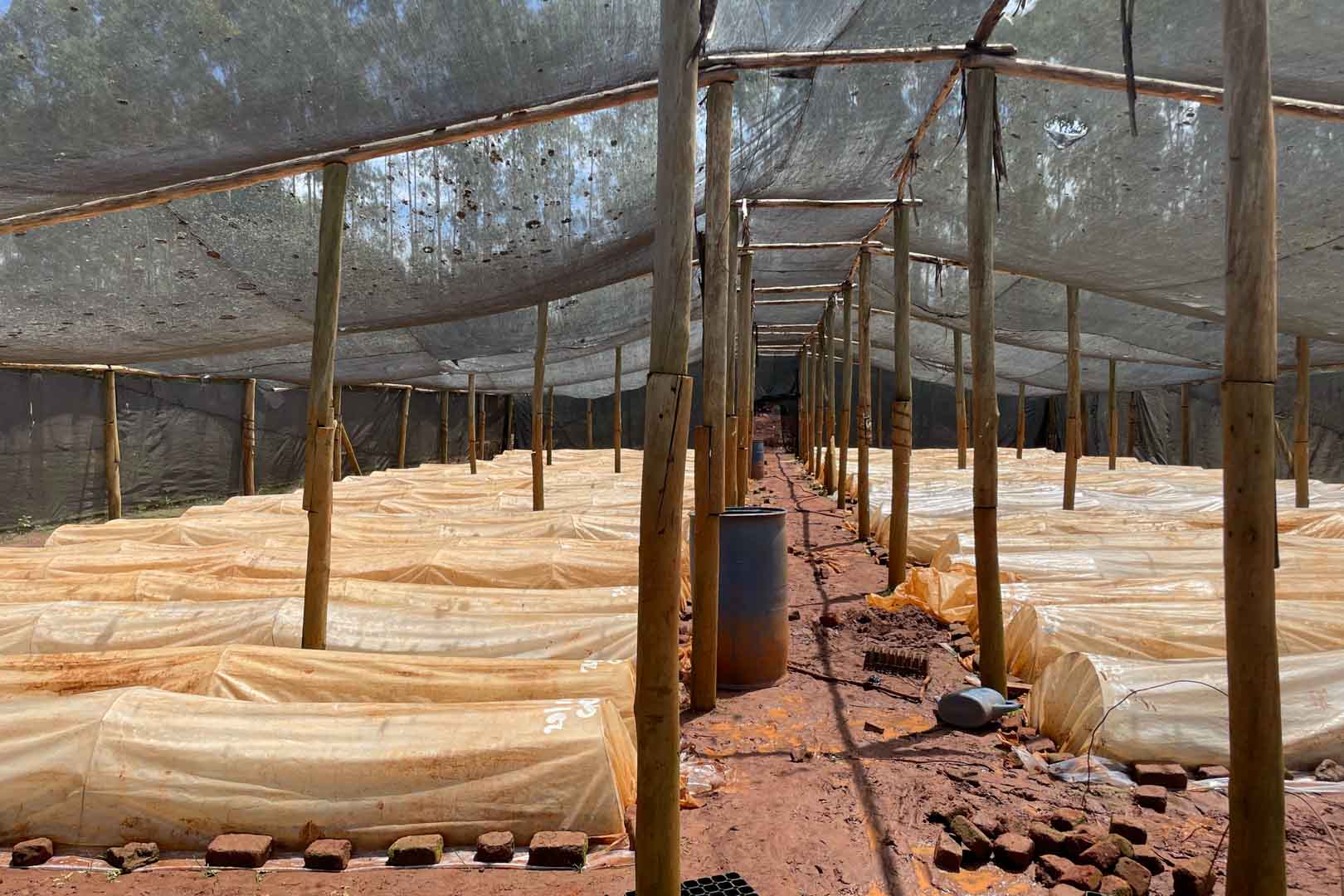
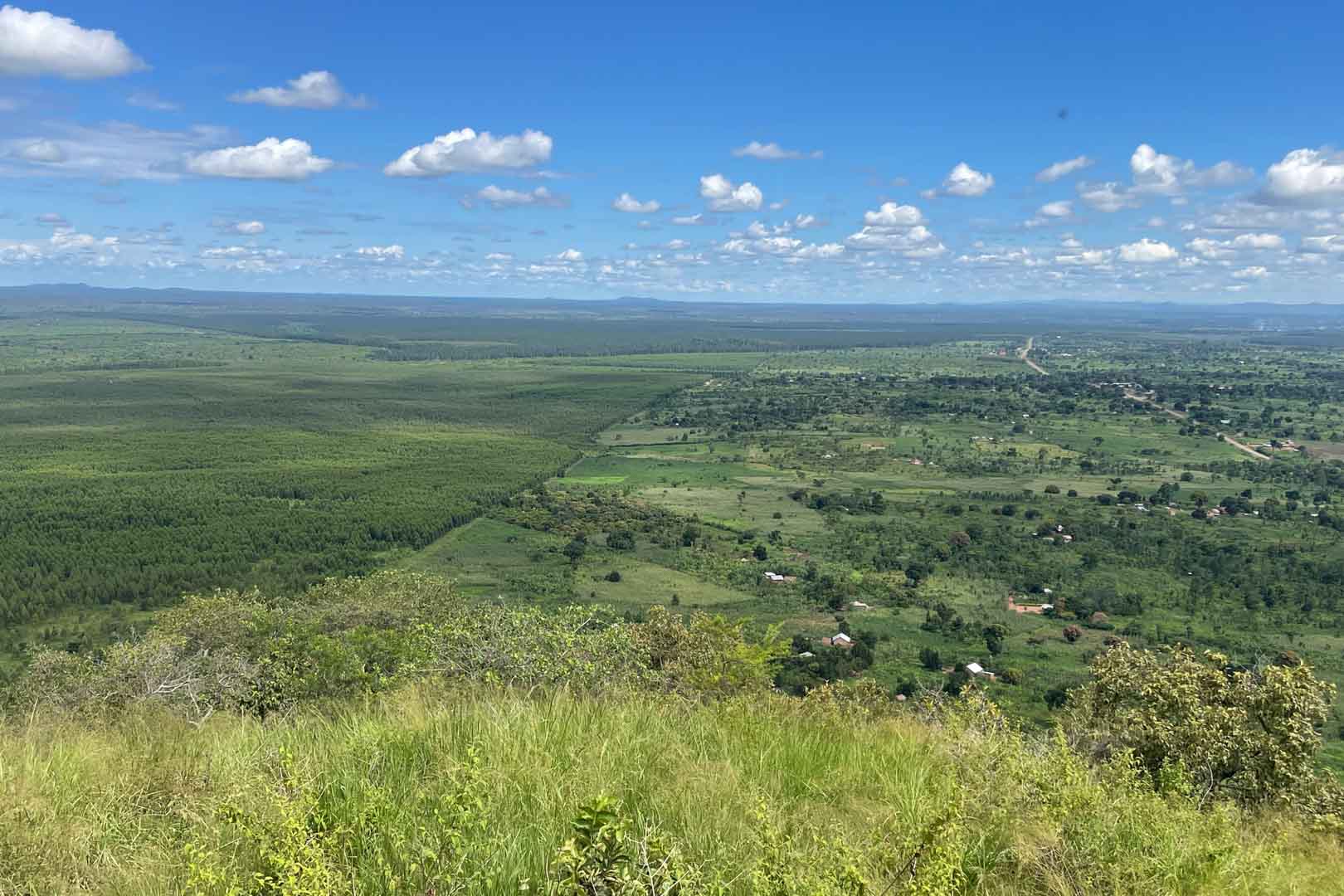
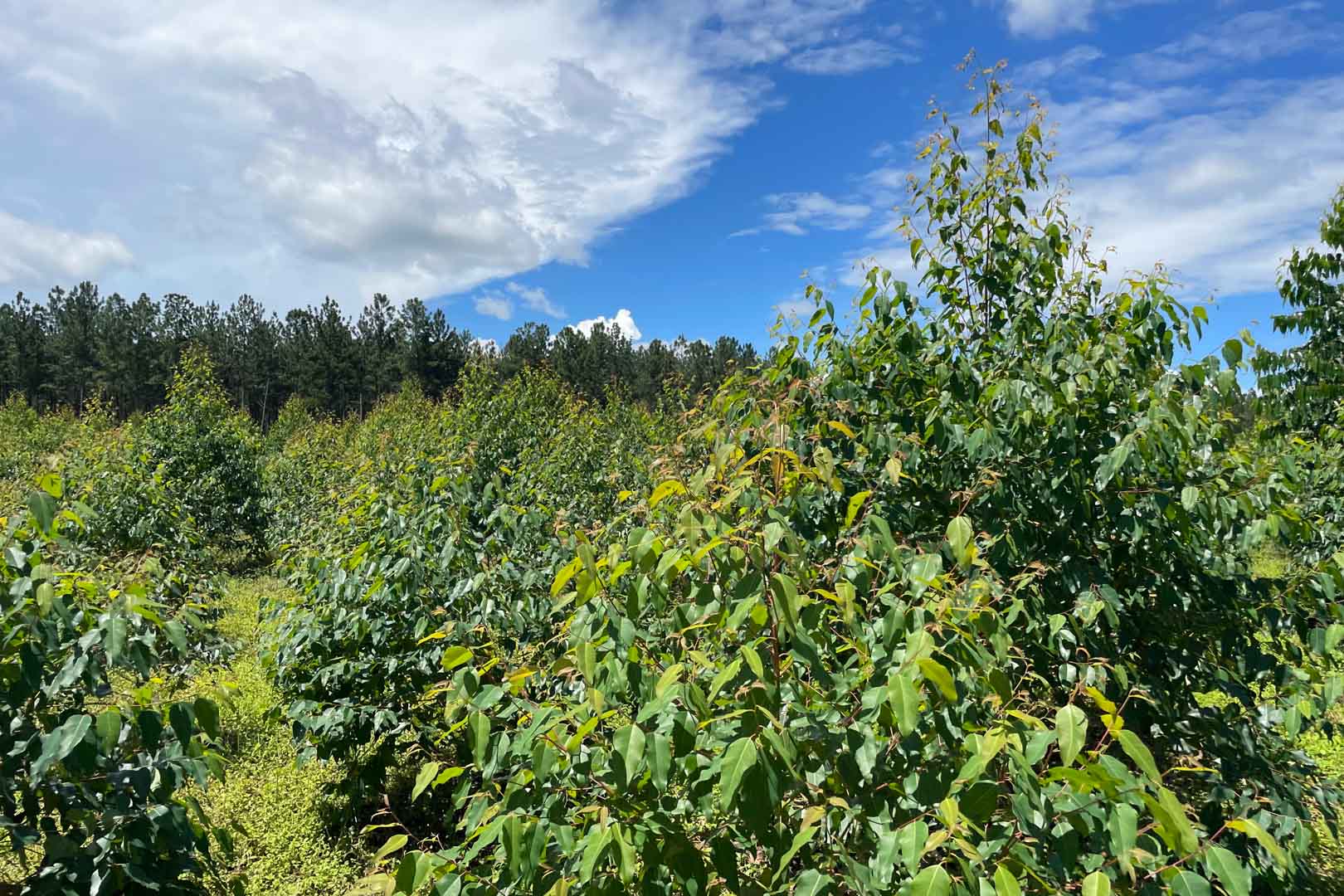
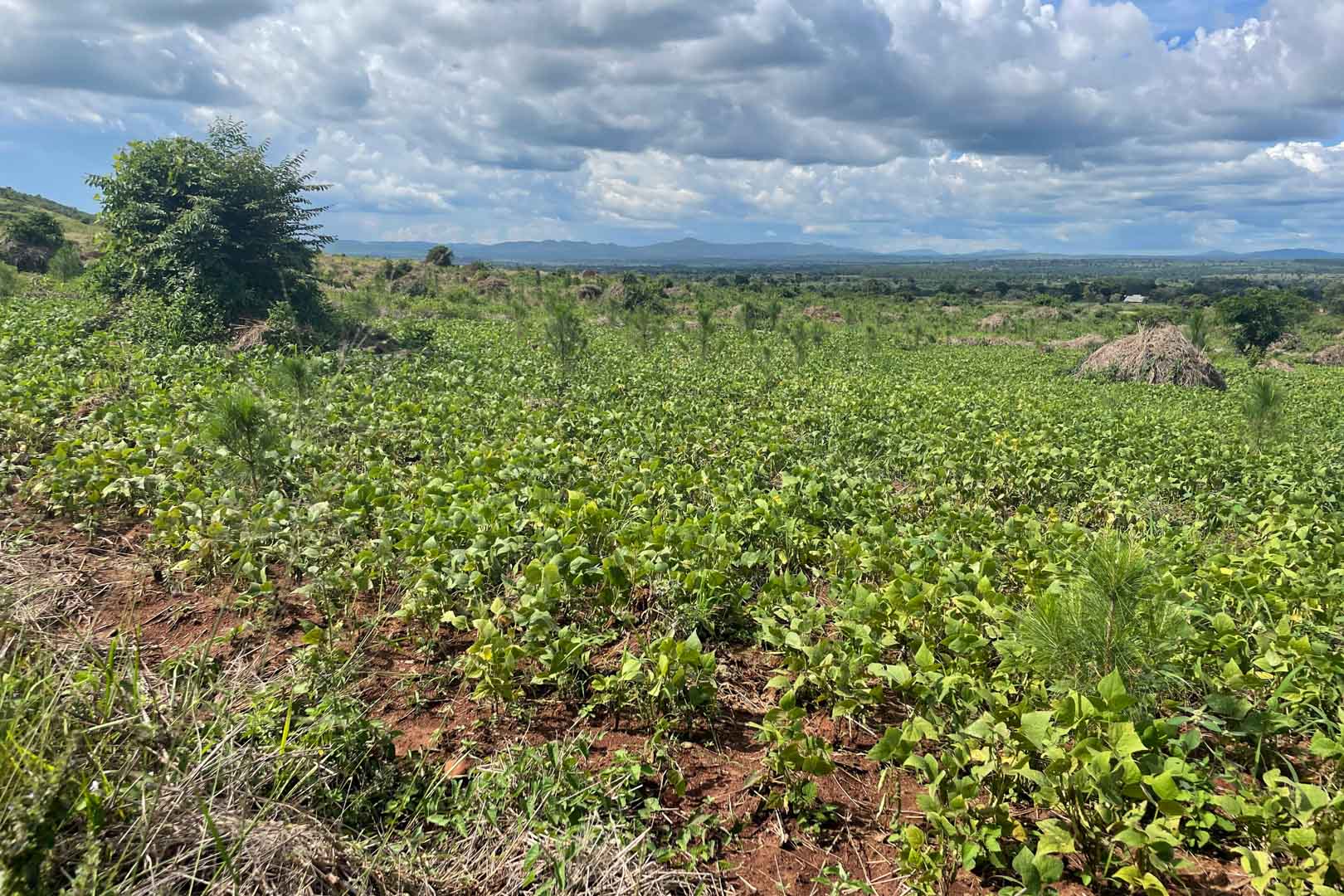
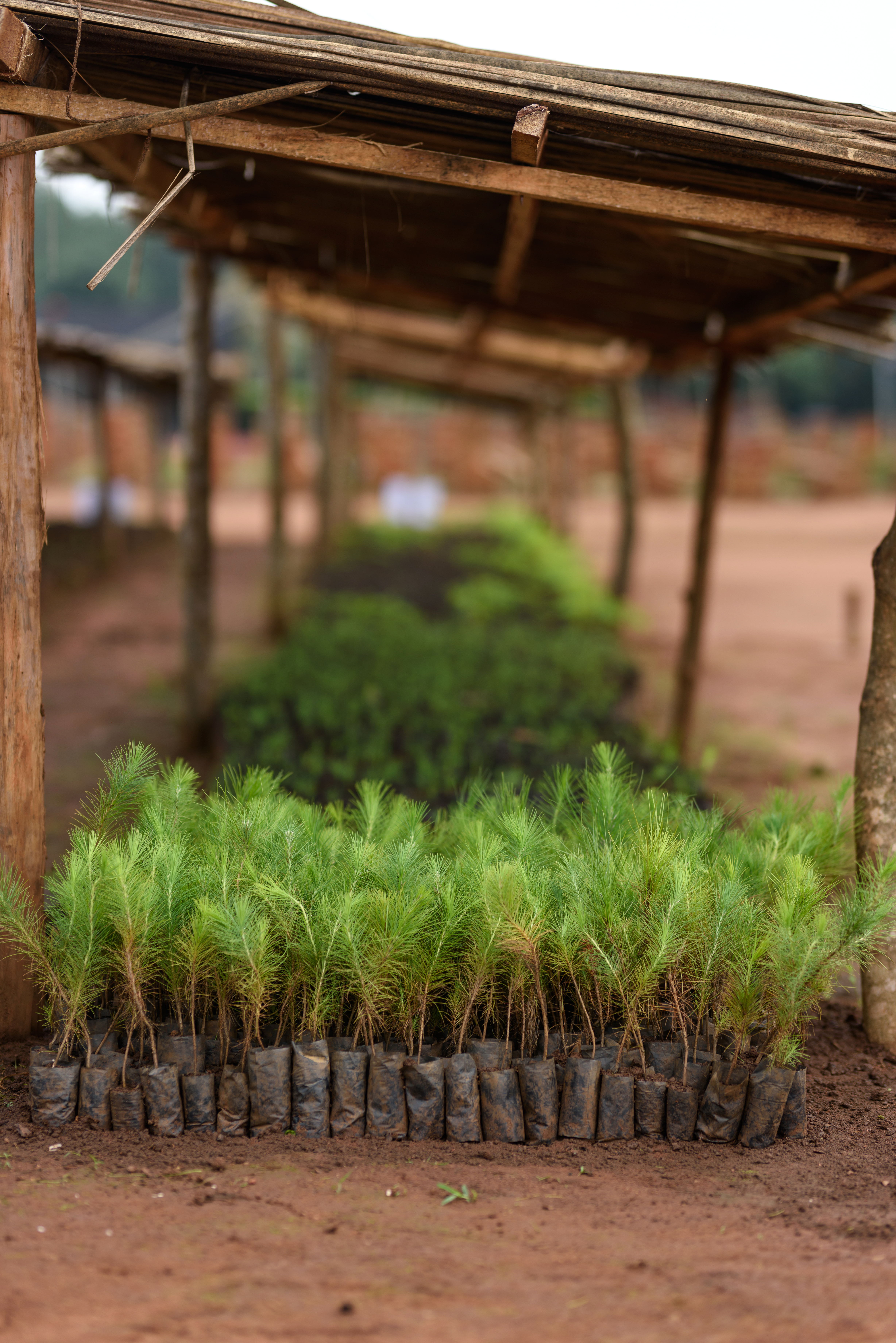
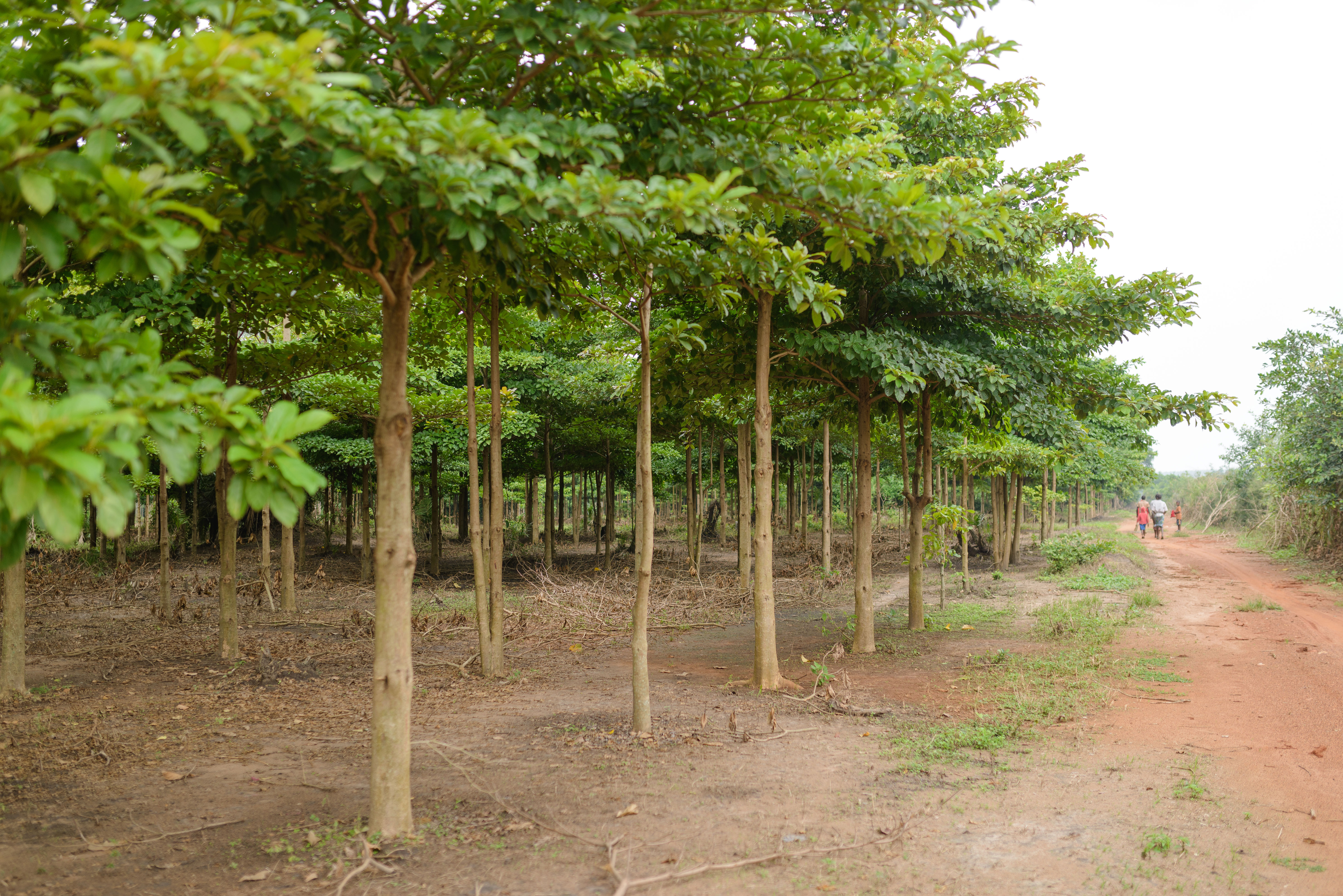
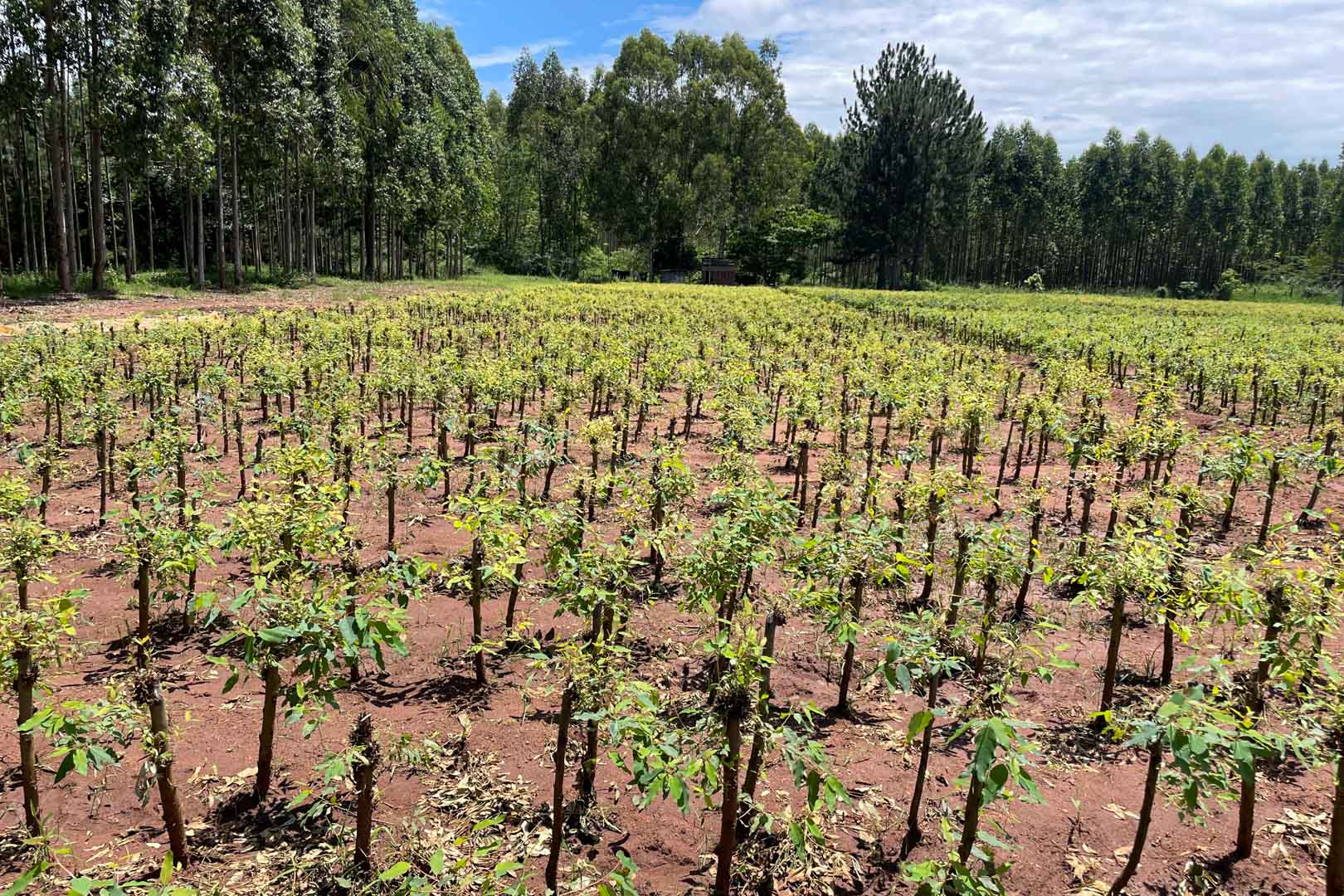
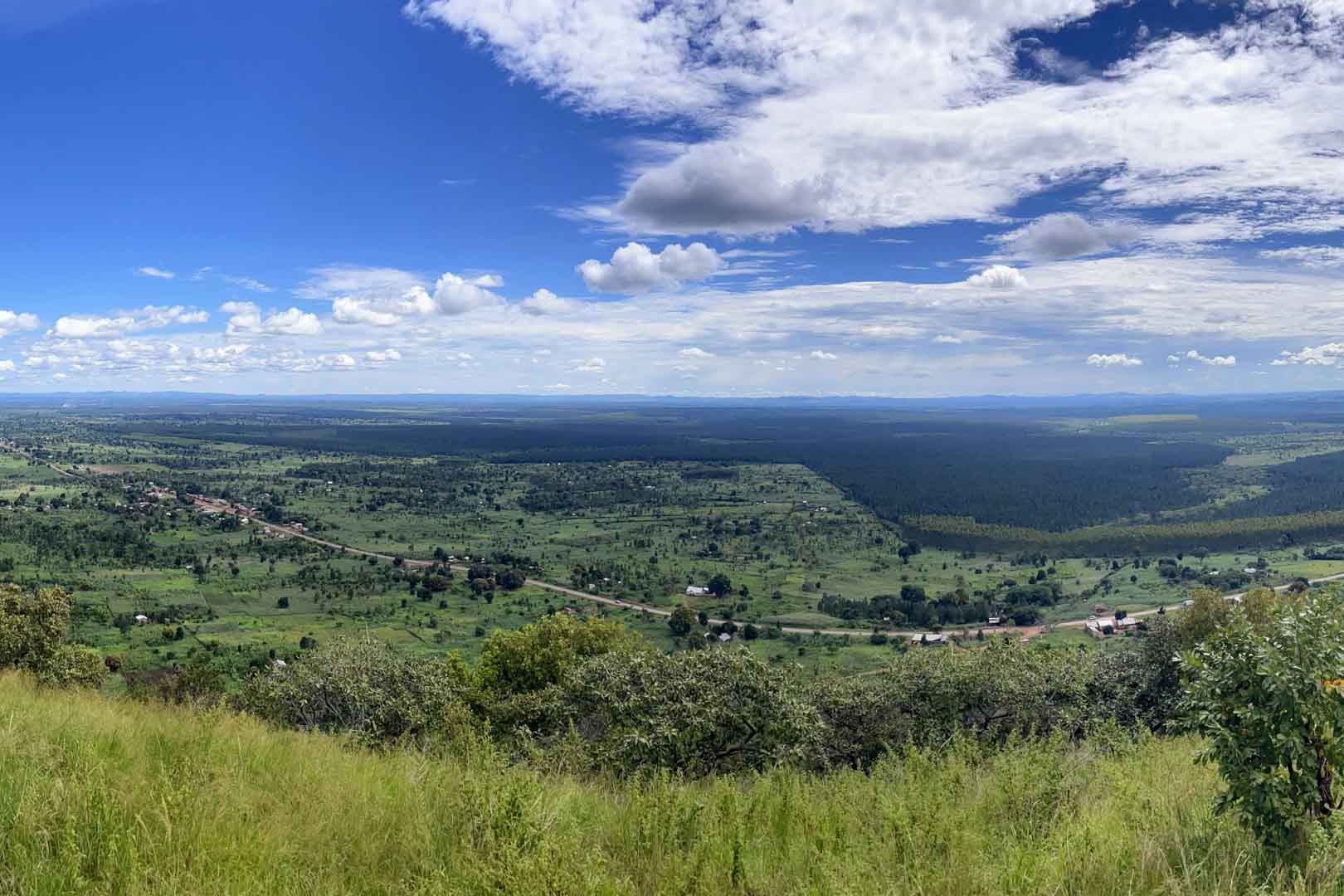
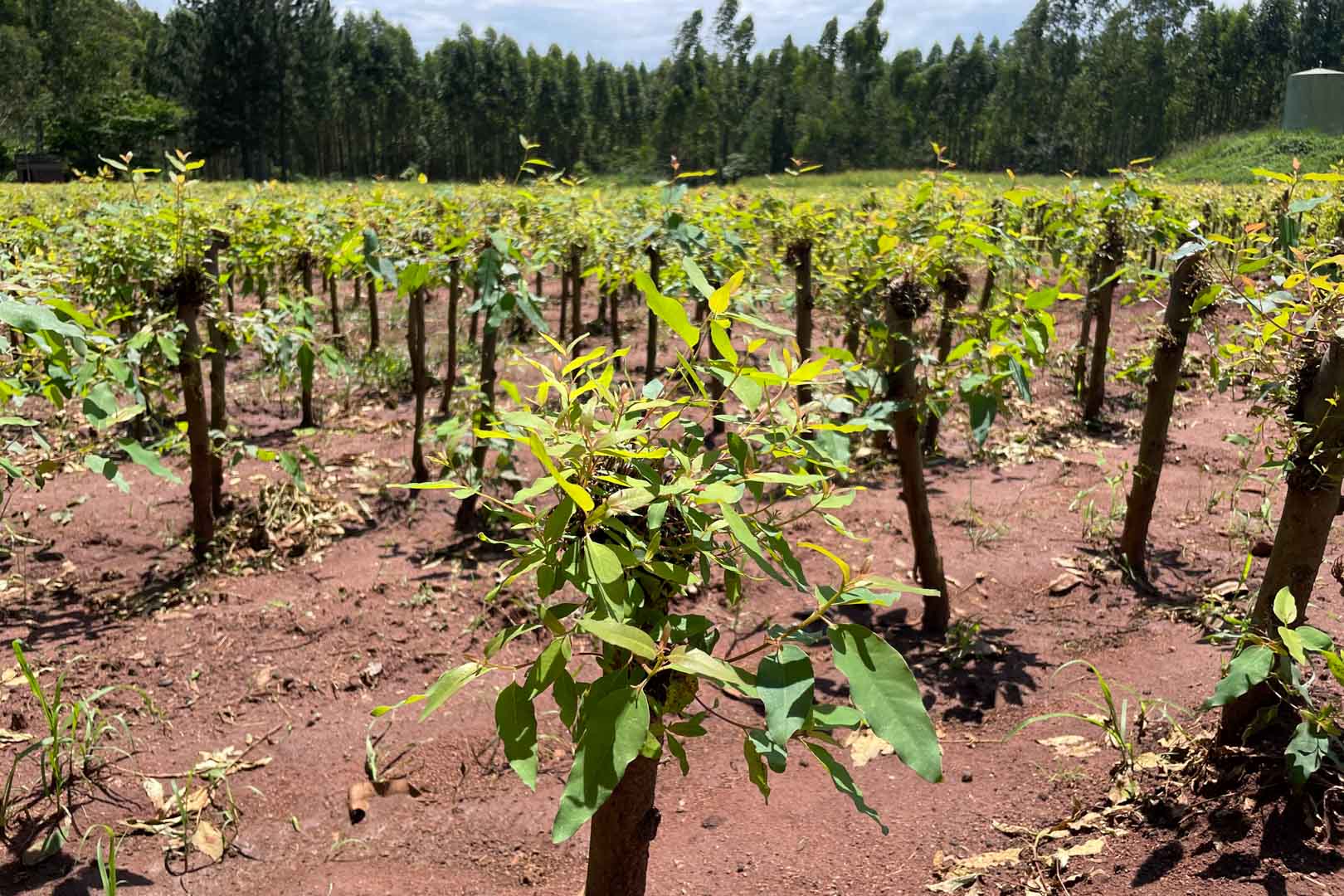
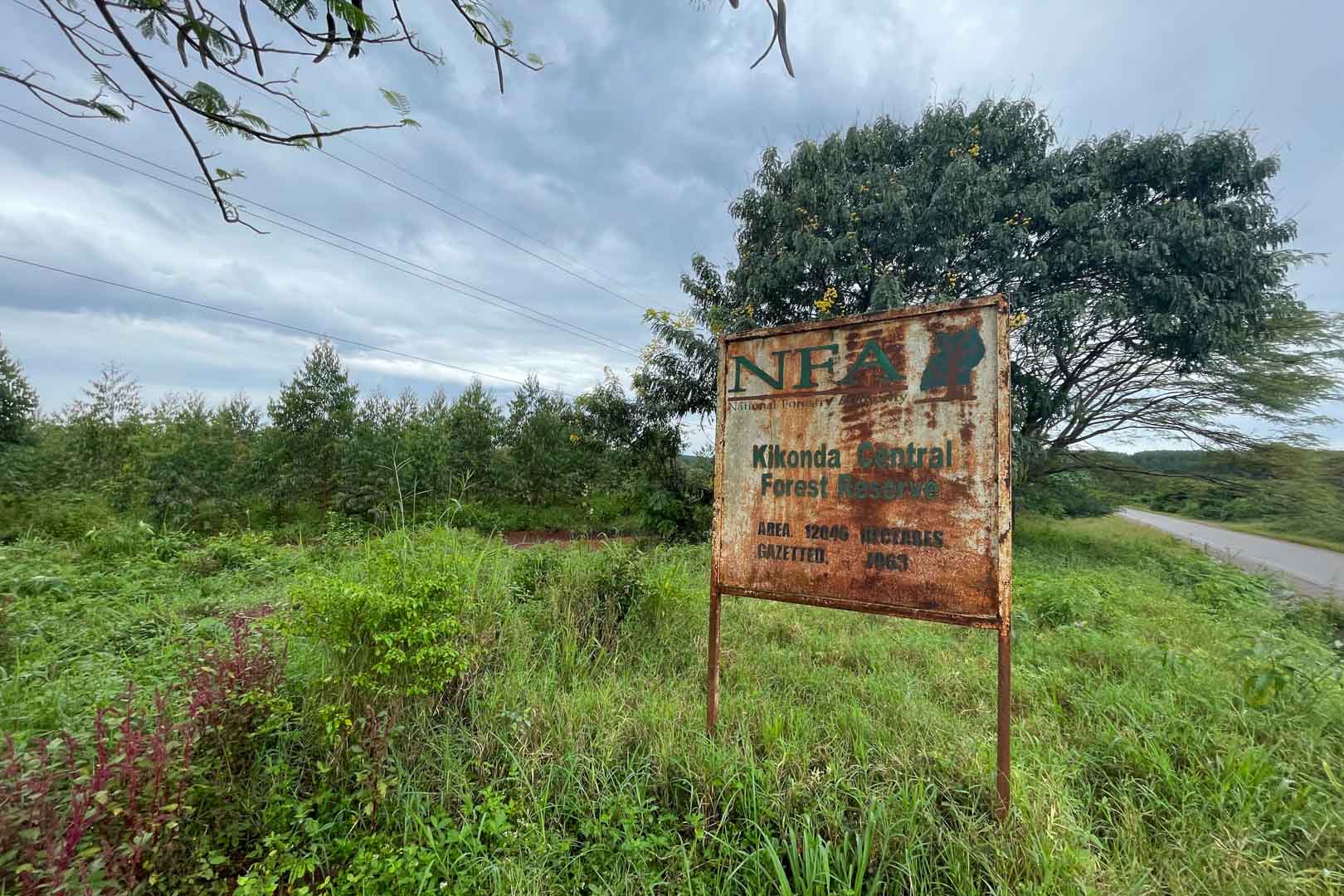
In the project area, which covers more than 10,000 hectares, afforestation is taking place in areas where uncontrolled deforestation had previously taken place. In particular, Caribbean pine and native species are used. The Gold Standard project supports the population of the surrounding settlements with the help of a training program that teaches them single-handed tree planting and nurturing.
Currently, the project in Kikonda is combined with the following projects registered under the Clean Development Mechanism (with CERs):
Biomass, Heilongjiang, China (#1411)
Wind power, Karnataka, India (#1394)
Wind power, Tirupur, India (#1493).
This high-value project combination allows the project in Uganda to be pre-financed with Planned Emission Reductions (PERs) under the terms of ICROA.
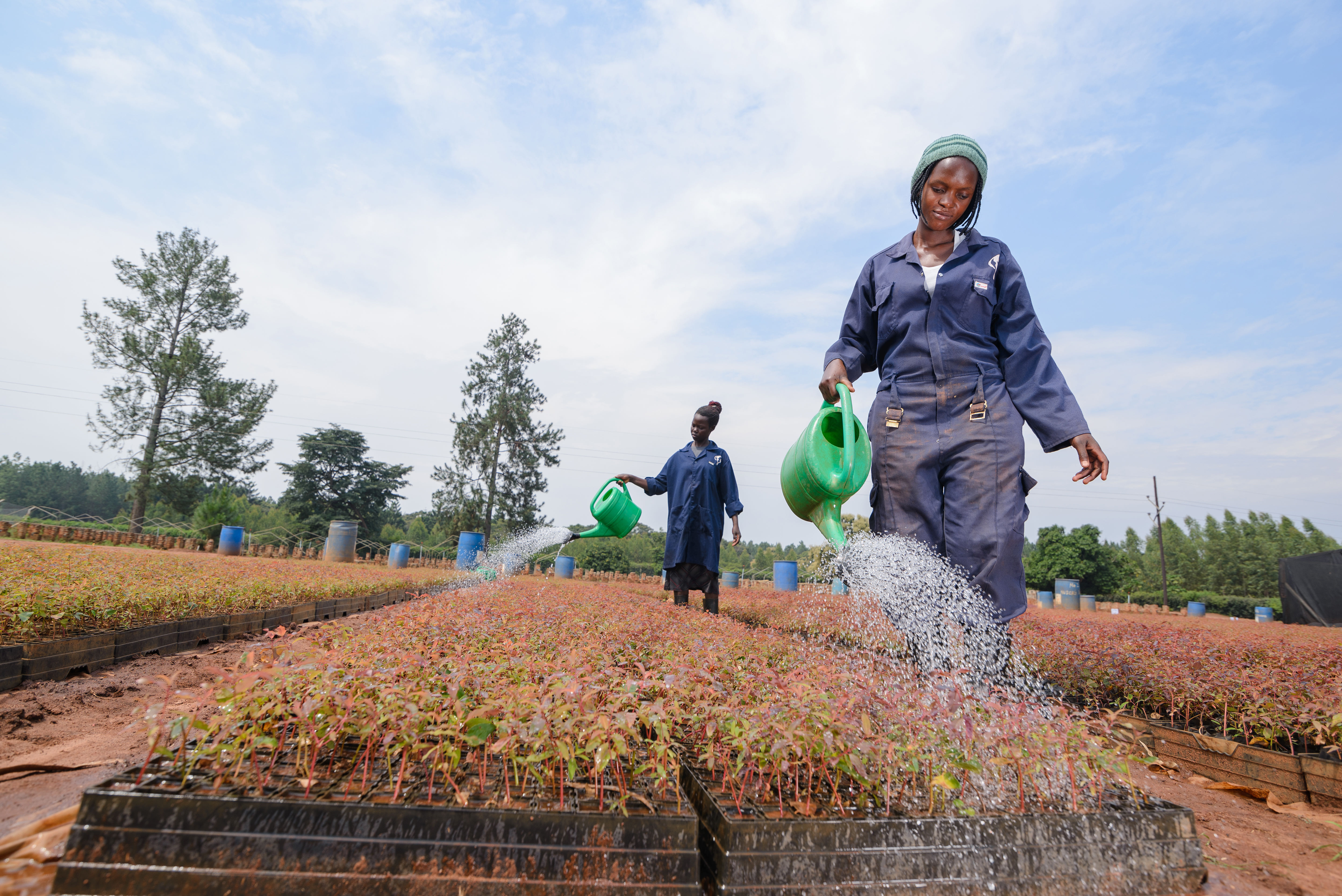

Forests are essential in our lives and are among the planet's most important carbon sinks. Besides providing habitats for wildlife, they filter the air, stabilise and protect soils, store water, and contribute to the balance of our climate. However, global forest areas have declined sharply in recent decades due to increasing settlements, agriculture, illegal logging, and raw material extraction. Afforestation, reforestation, and revegetation activities significantly increase a forest’s carbon storage capacity in both the biomass of the forest and in the soil. The storage capacity varies according to the tree species, age, and location. Experts distinguish these activities in the following way:
Afforestation converts non-forested areas into forest ones. Reforestation restores forest areas that have been damaged or deforested in the past. Revegetation increases the vegetation through planting trees, shrubs, or other plants.
What’s a combined project?
With combined projects, ClimatePartner brings together funding for international, certified climate projects with additional support for nature conservation projects.
Explore our projects
Biochar for Climate Action, Healthy Soils, and Better Harvests

A certified climate project combined with additional commitment

Expansion of renewable energy generation in Asia
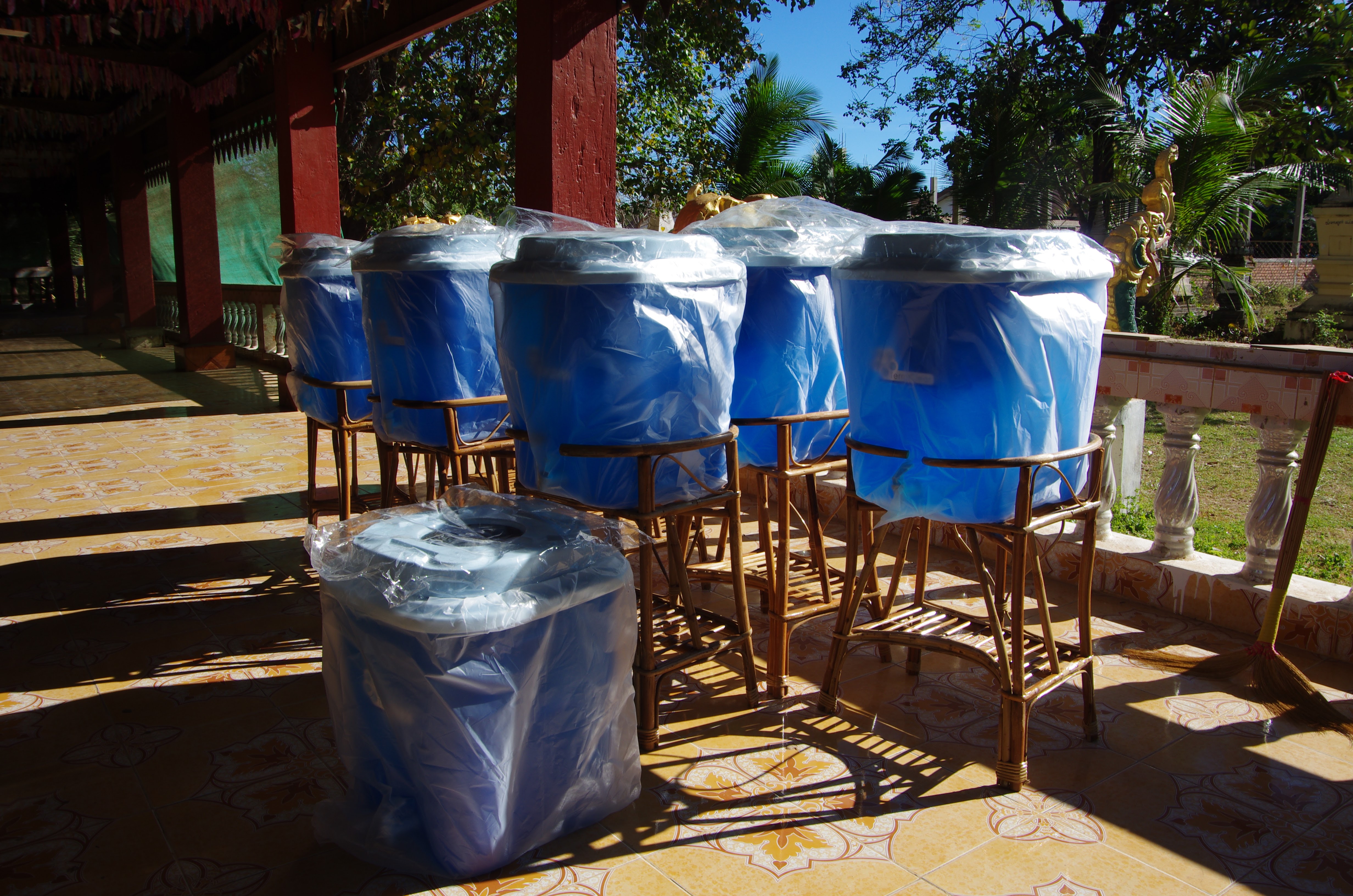

Ceramic water filters save CO2 and improve health
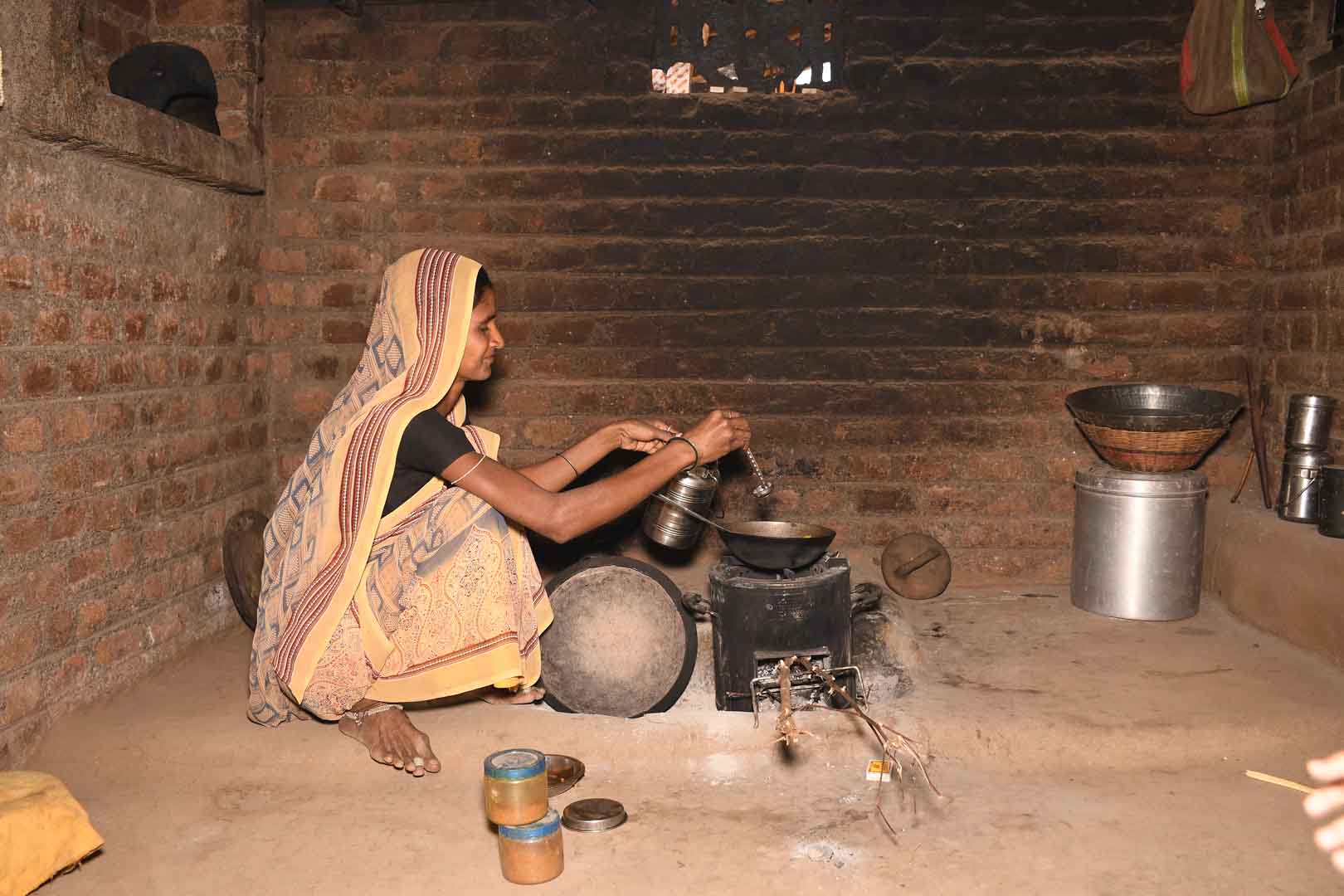

Improved cookstoves worldwide – for better health and cleaner air

A certified climate project combined with additional commitment
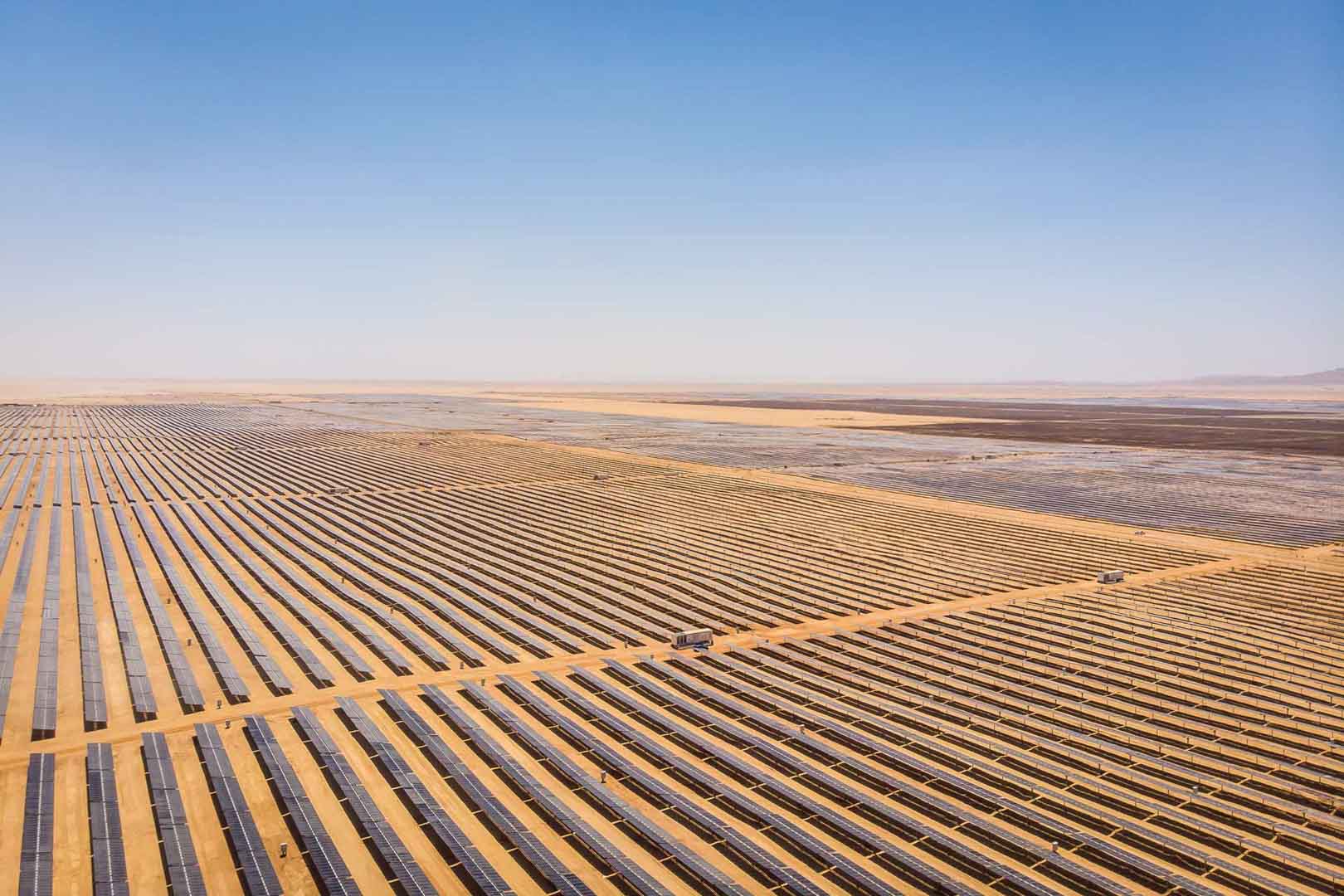

Powering access to renewable energy in Africa

A certified climate project combined with additional commitment

Restored ecosystems remove carbon
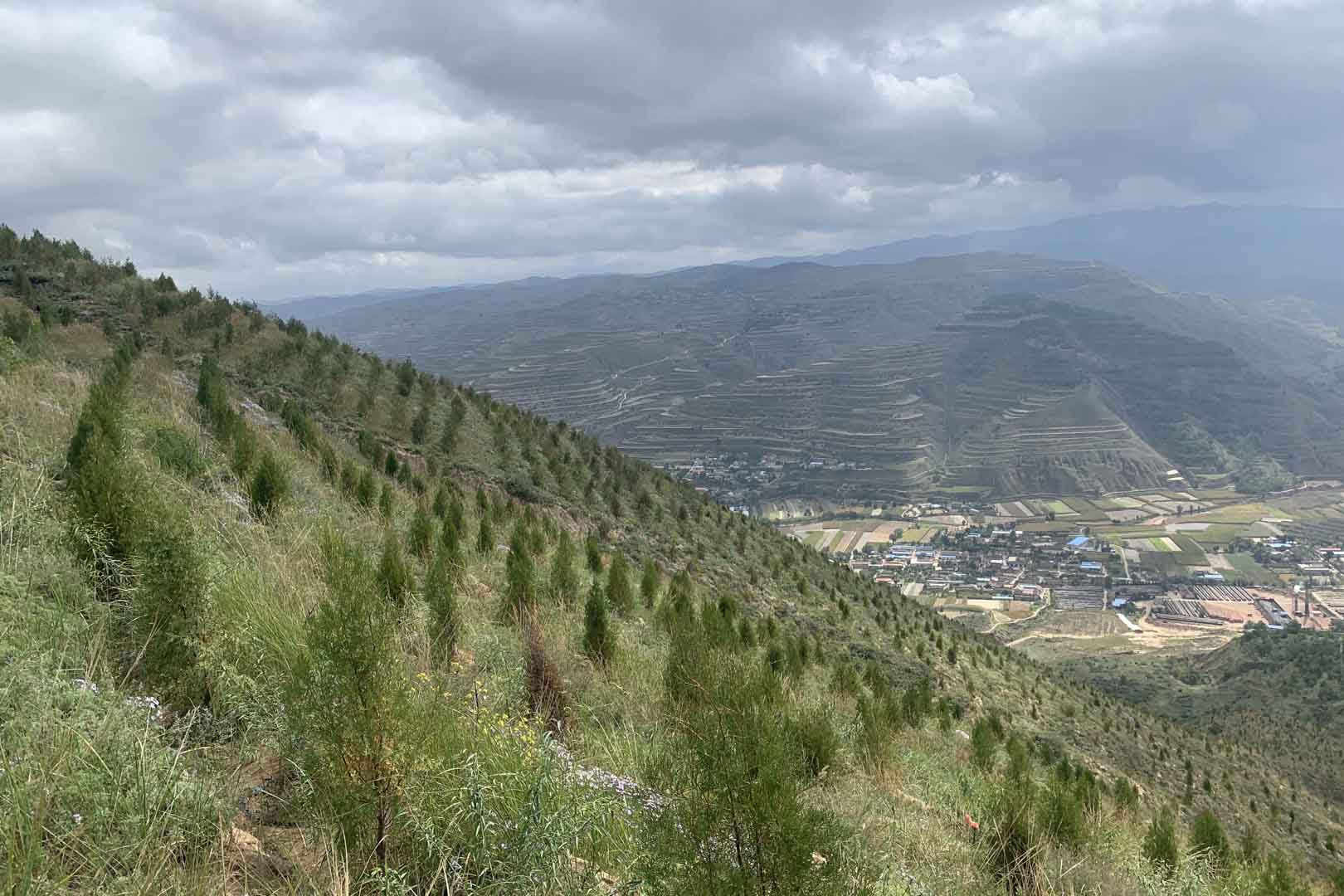

Turning degraded farmlands into healthy ecosystems
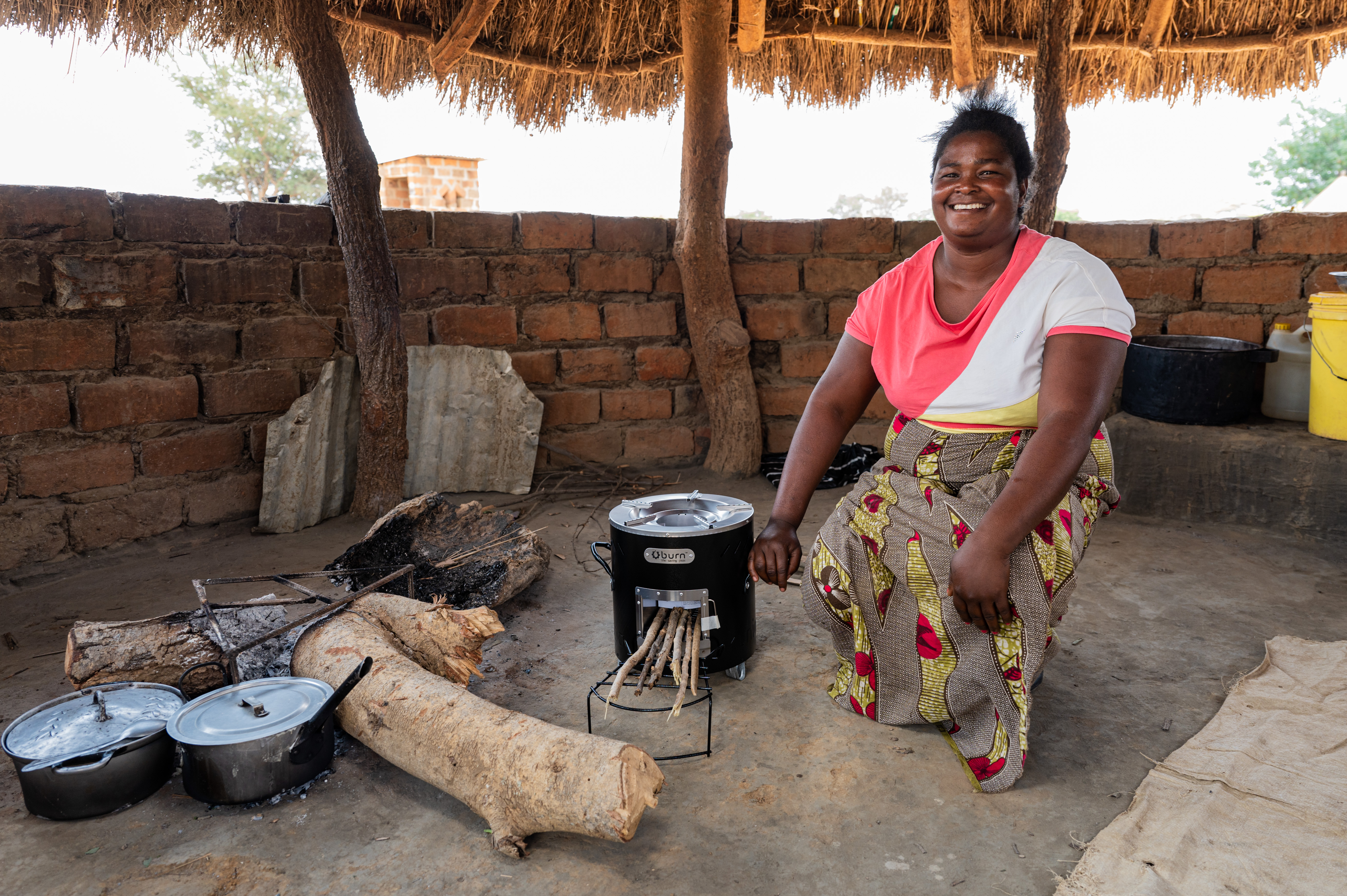

Improved cookstoves - better for health and the environment