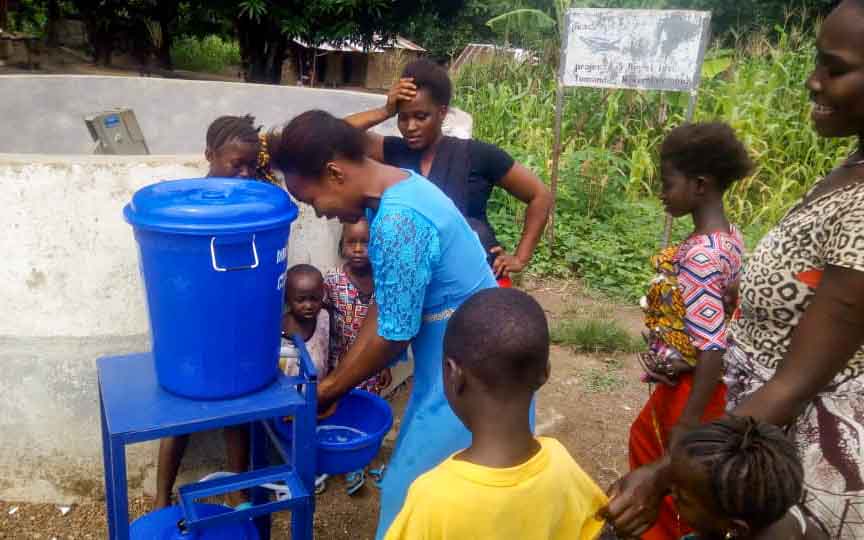Climate action through clean drinking water
Sierra Leone is a largely rural country where households typically use wood fuel on inefficient three-stone fires to purify their drinking, cleaning, and washing water. This process results in the release of greenhouse gas emissions from the combustion of wood – however, these emissions can be avoided by using efficient borehole technology that does not require fuel to supply clean water.
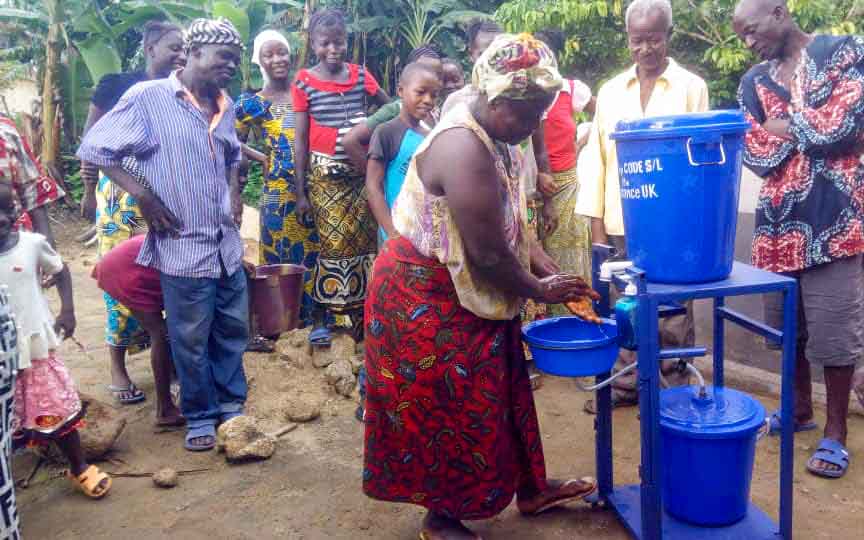
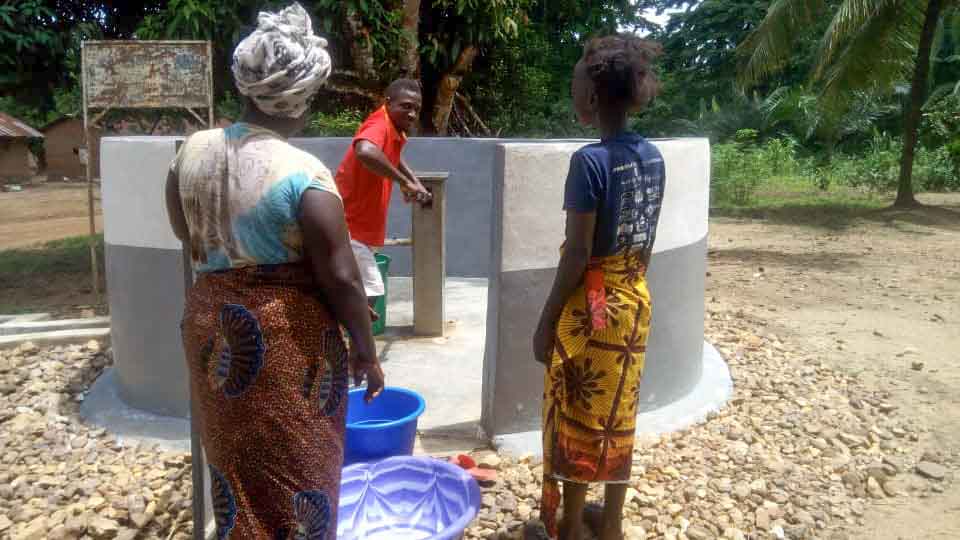
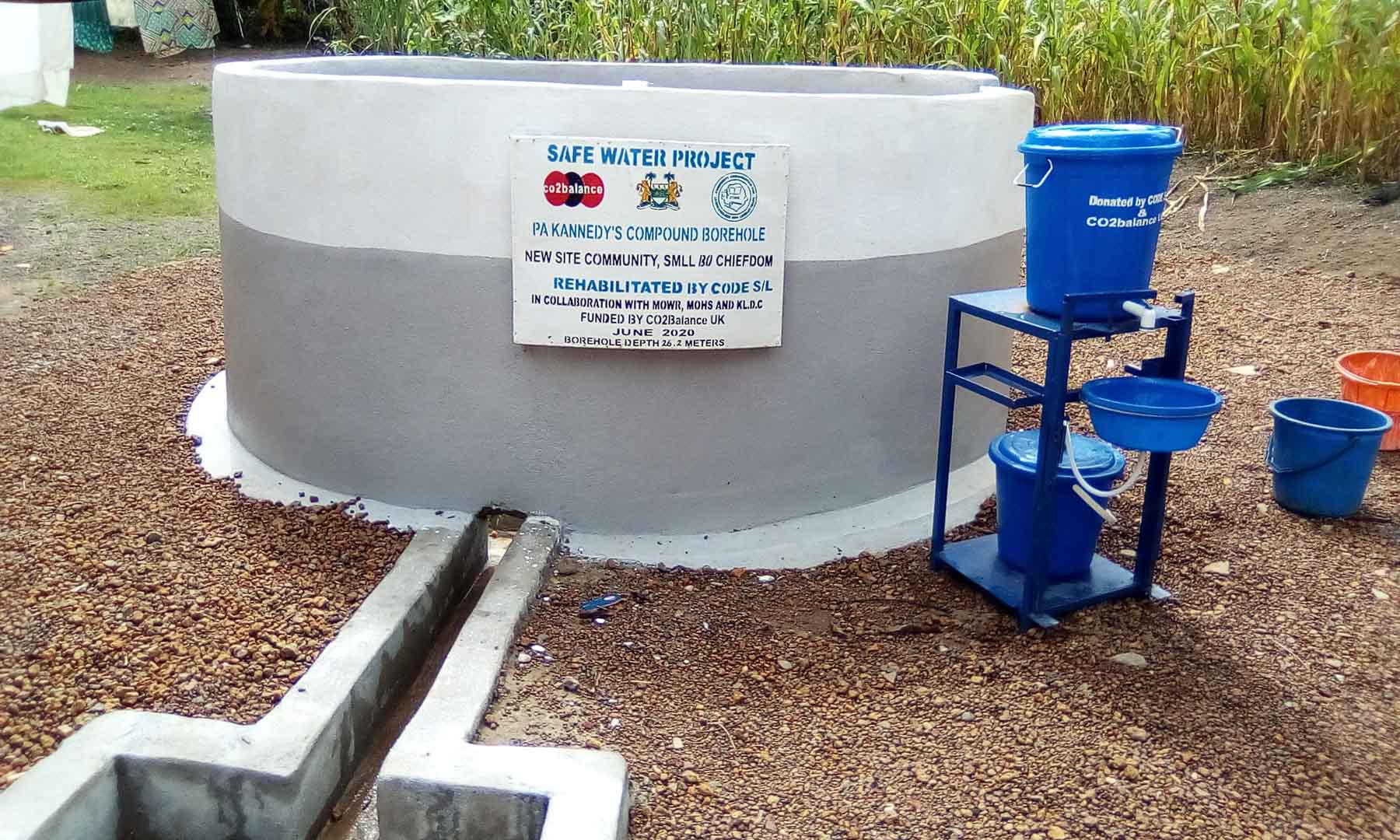
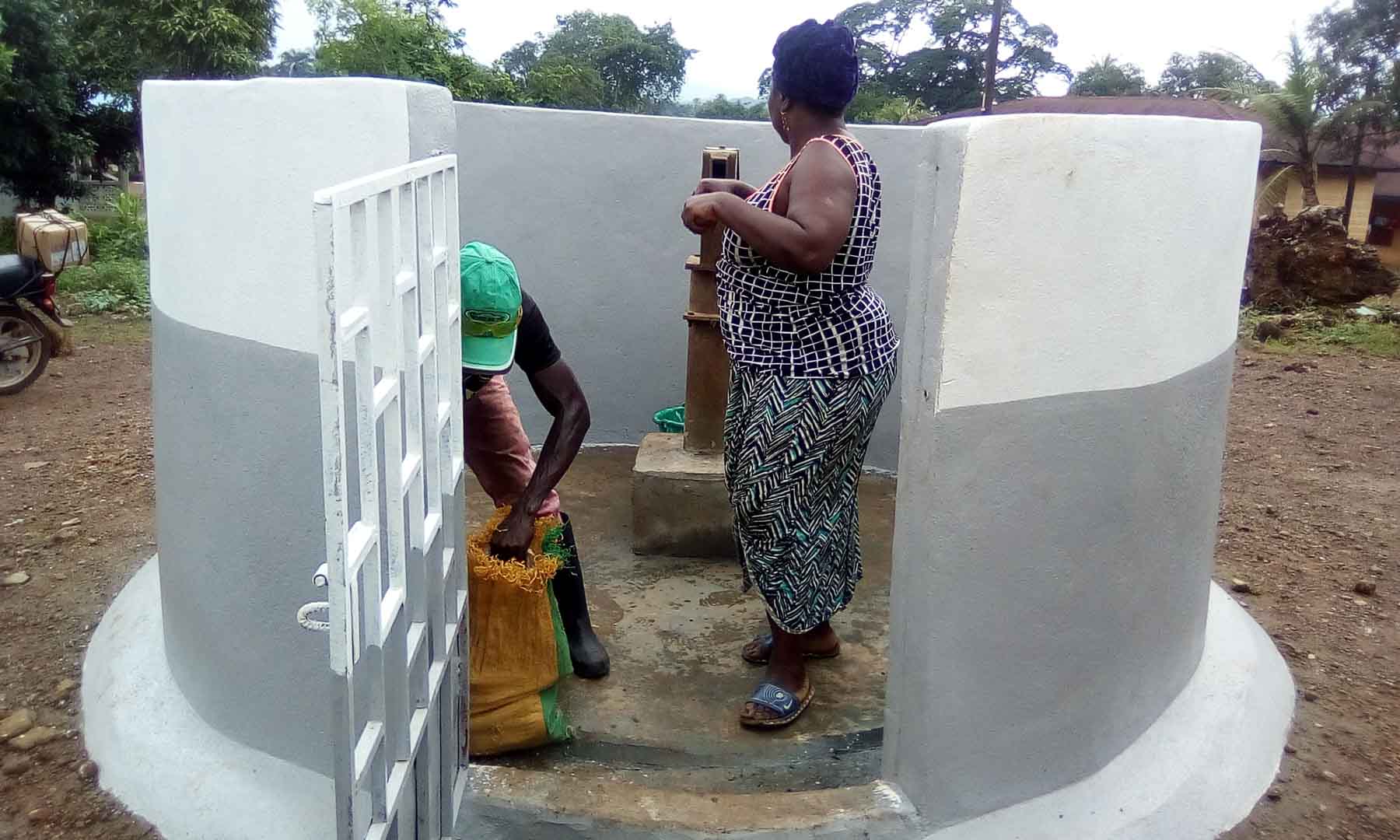
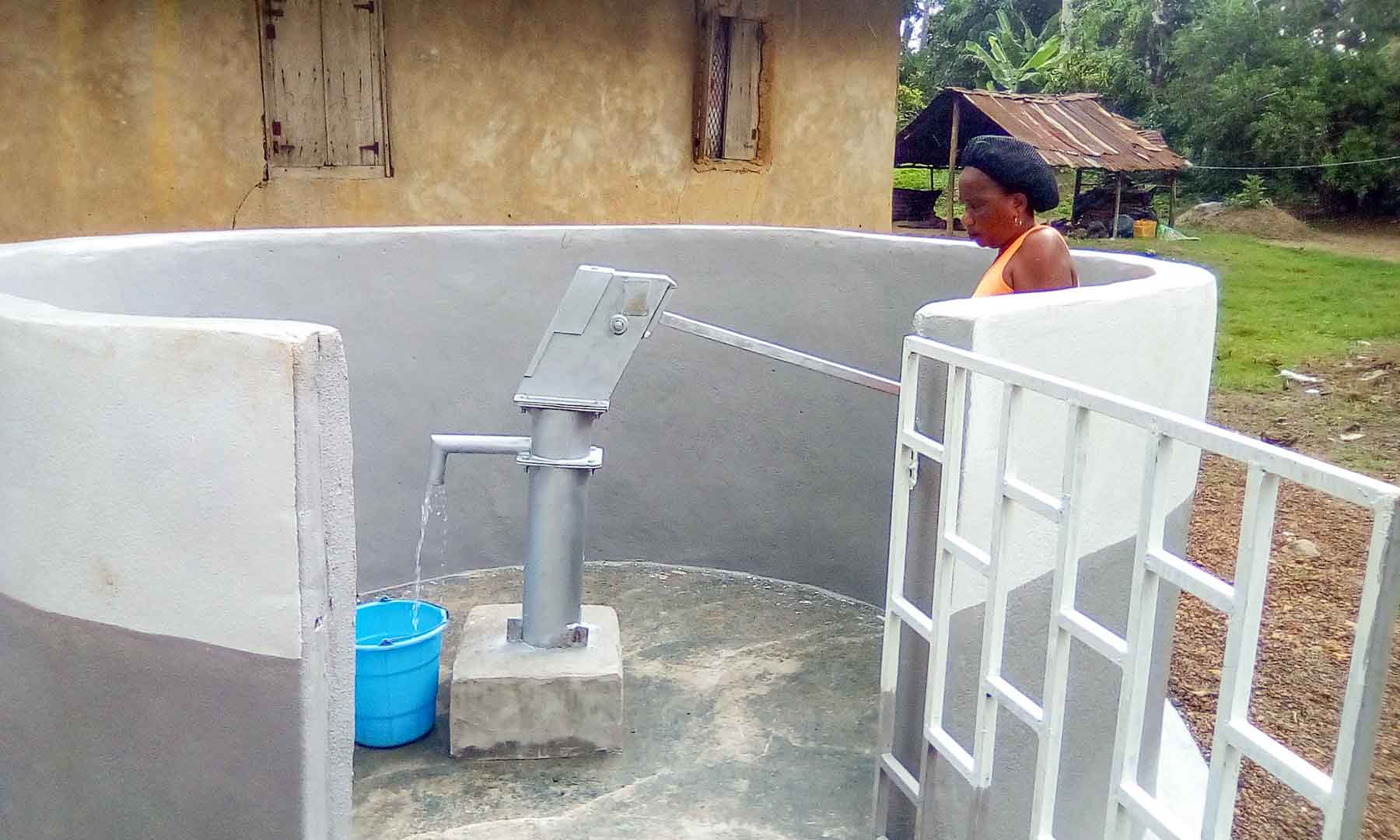
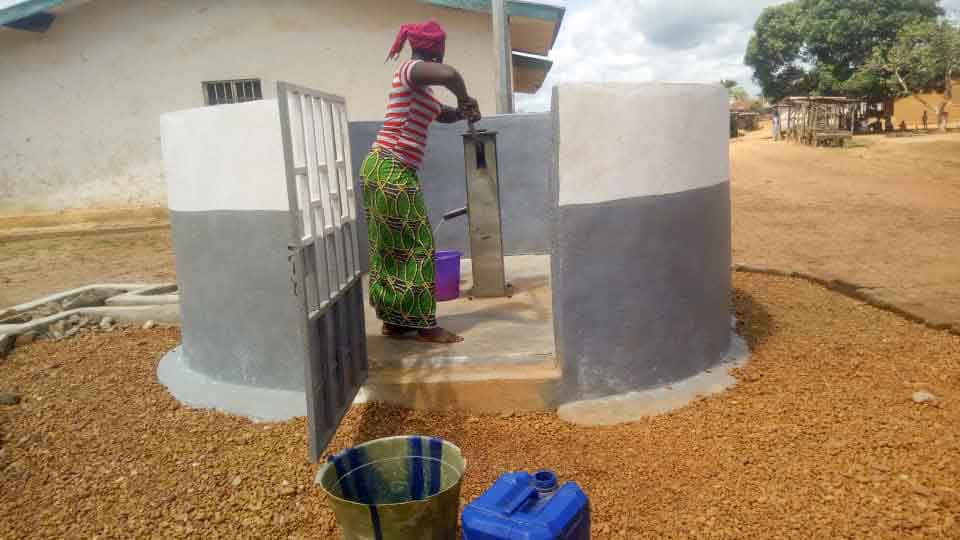
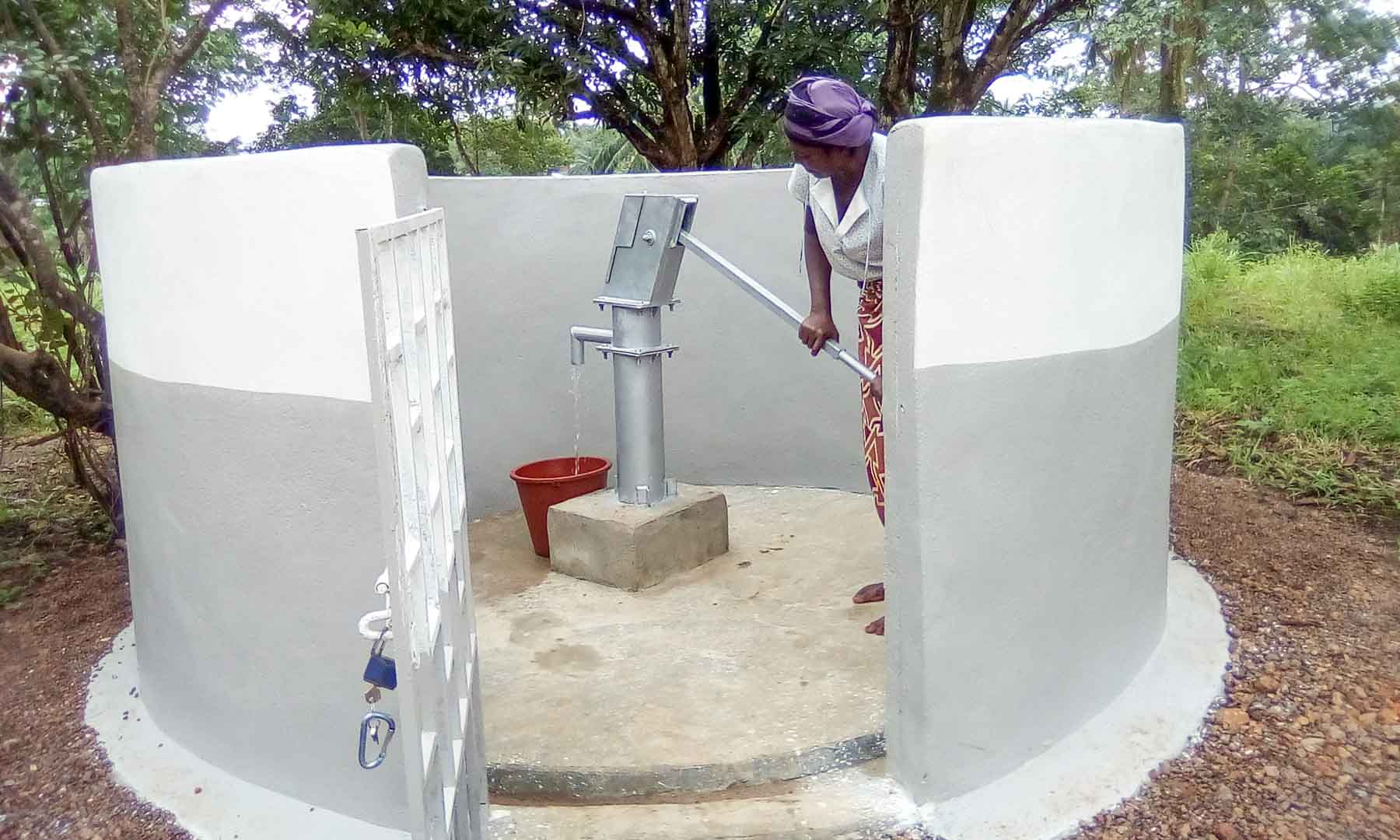
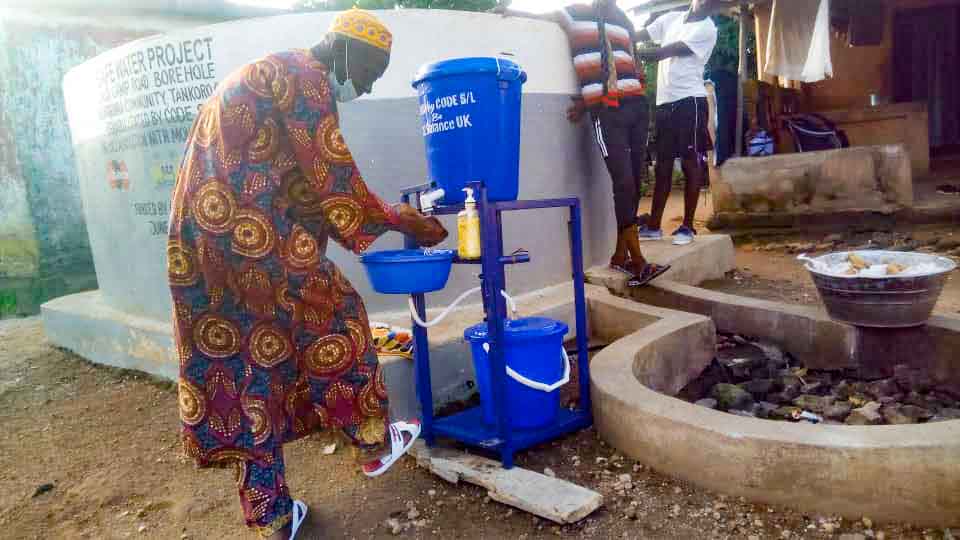
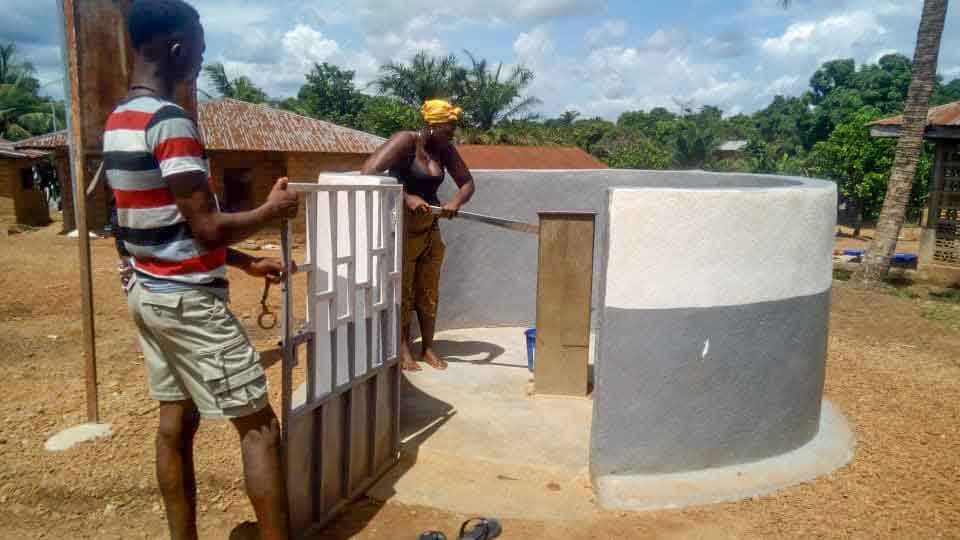
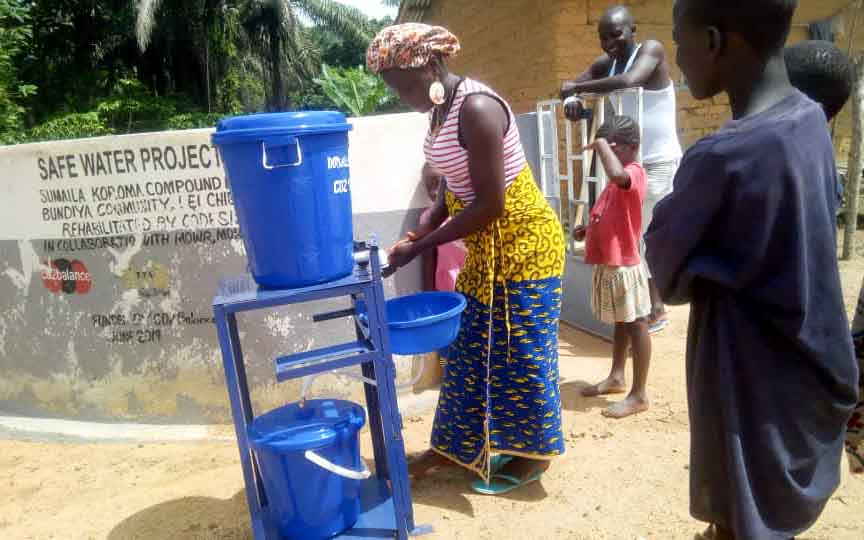
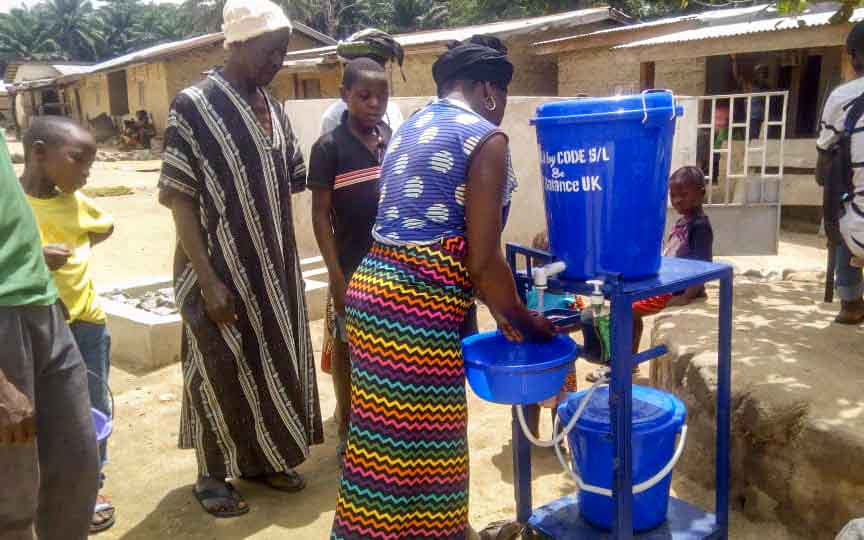
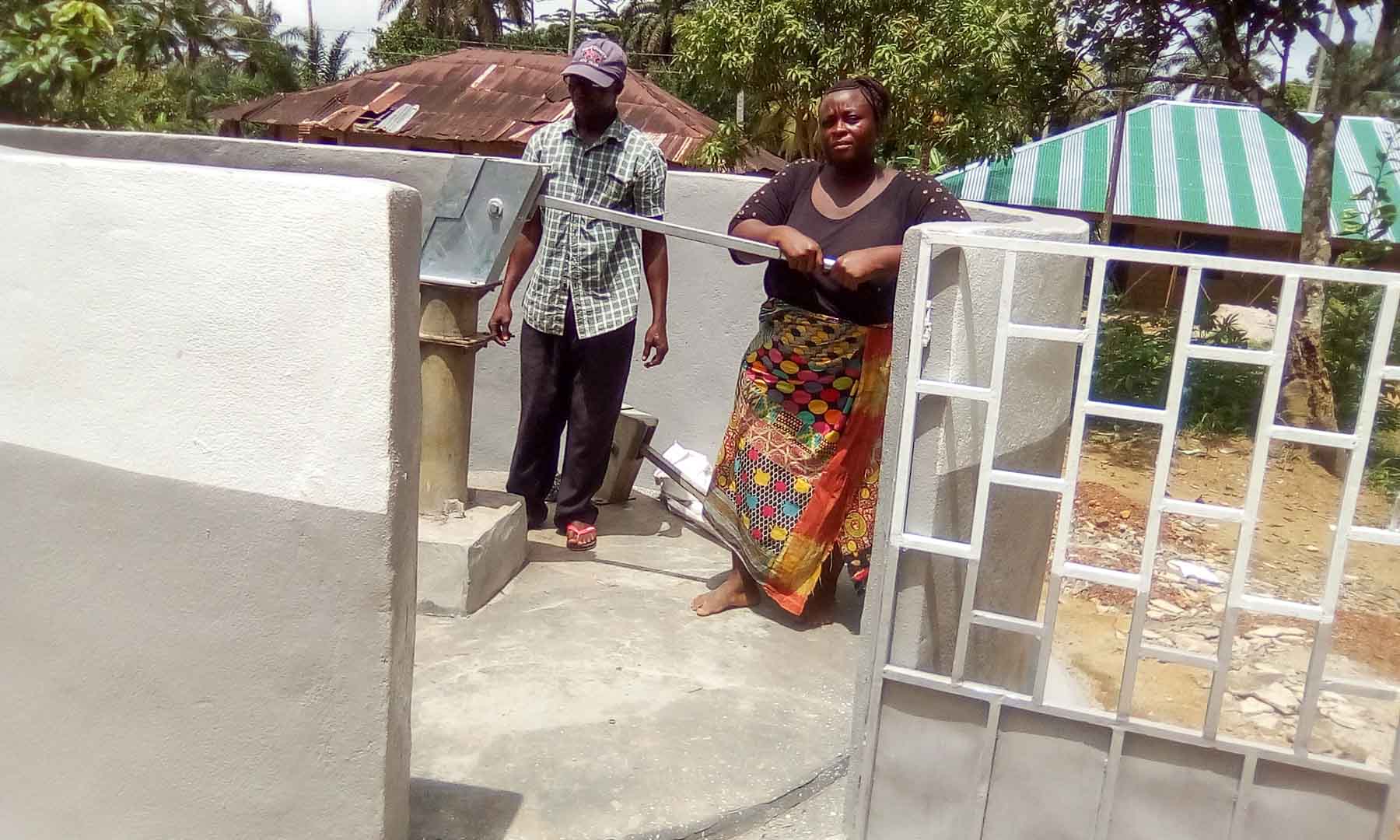
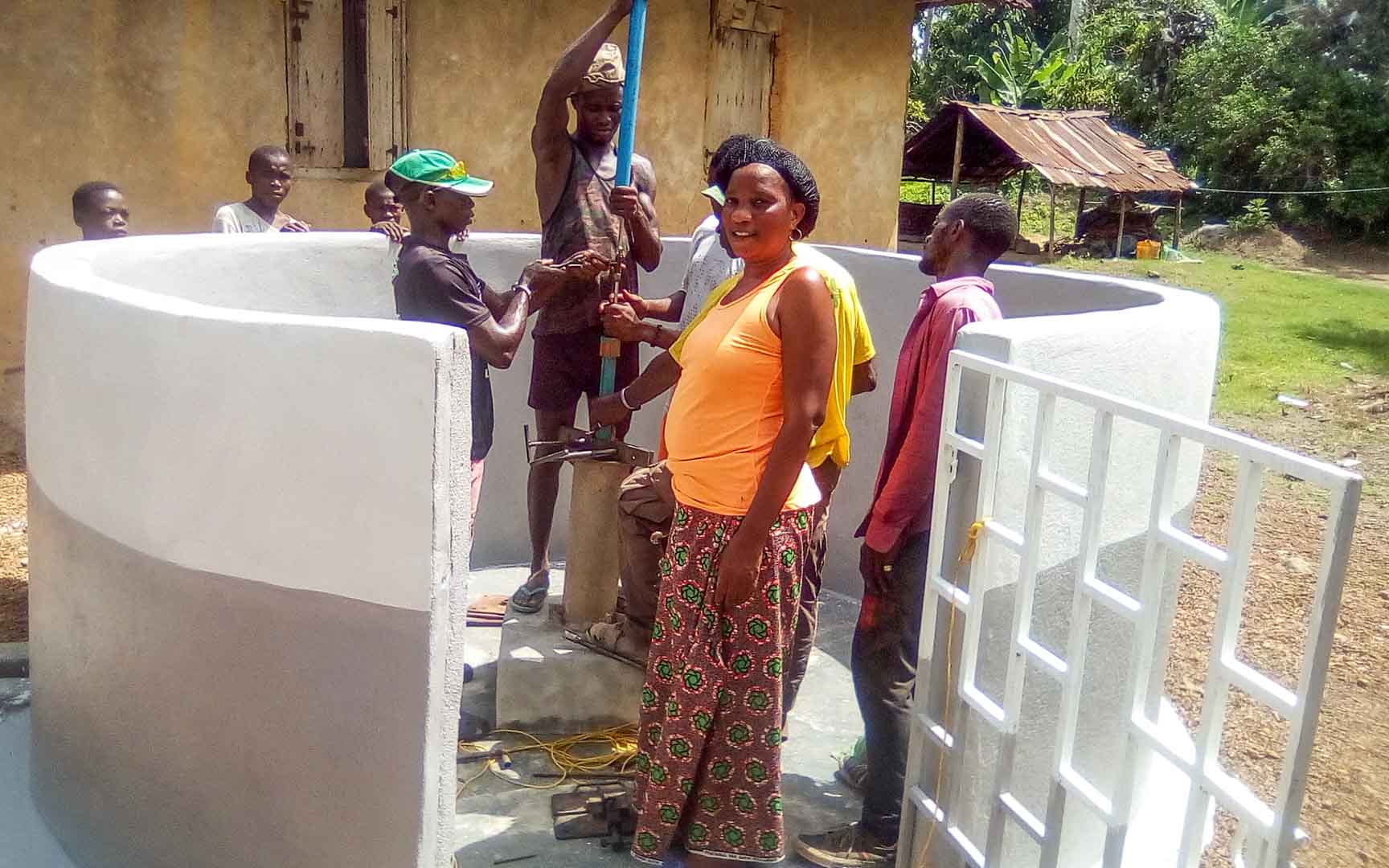
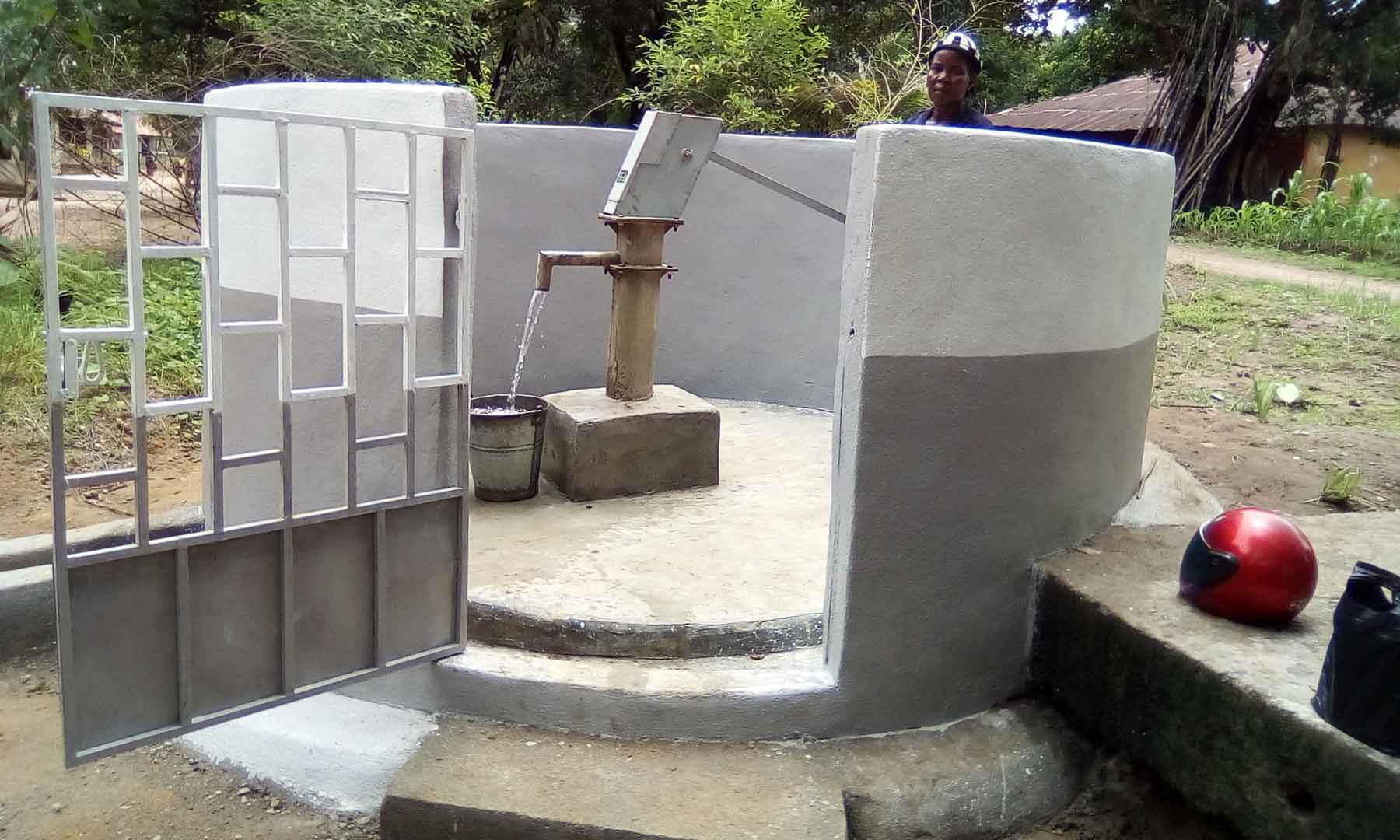
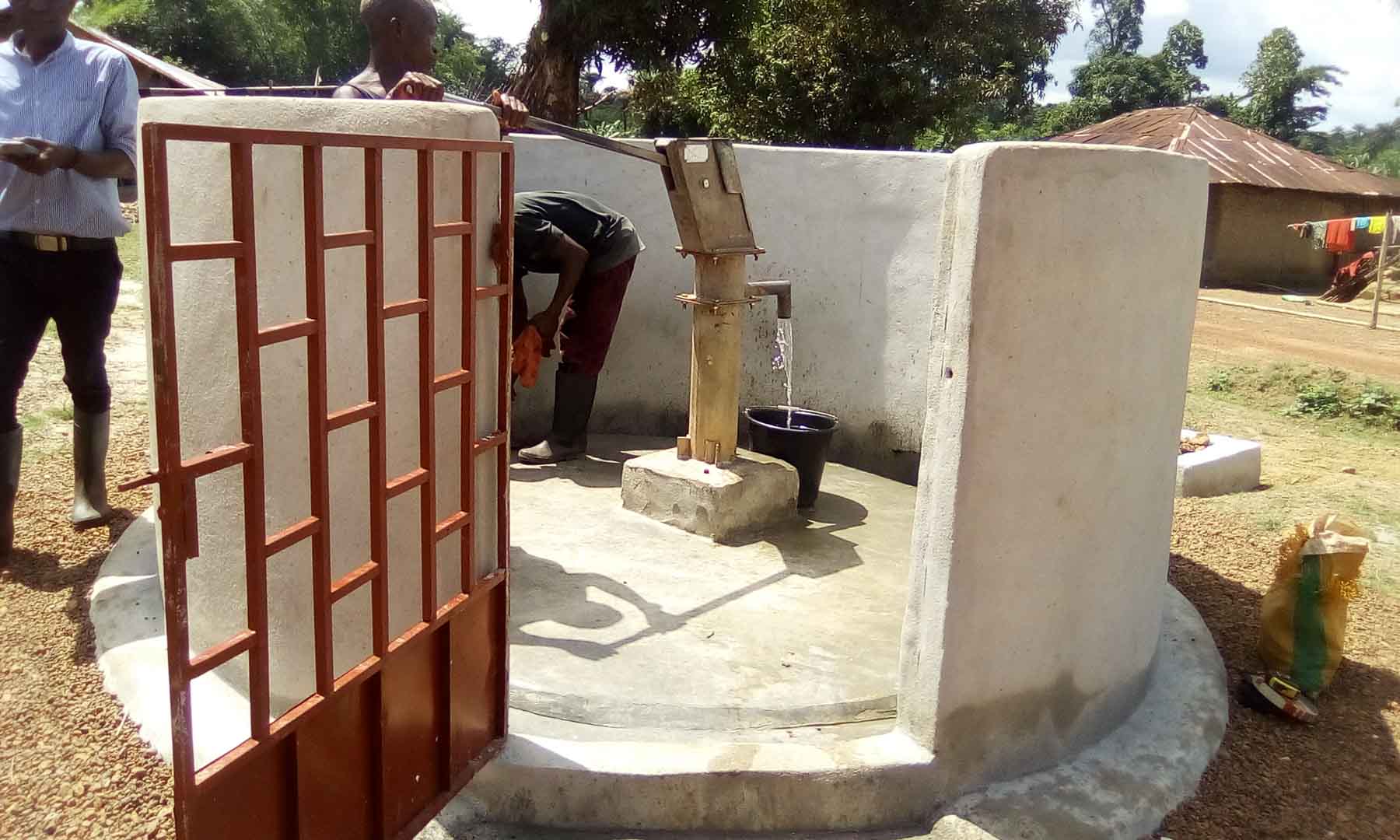
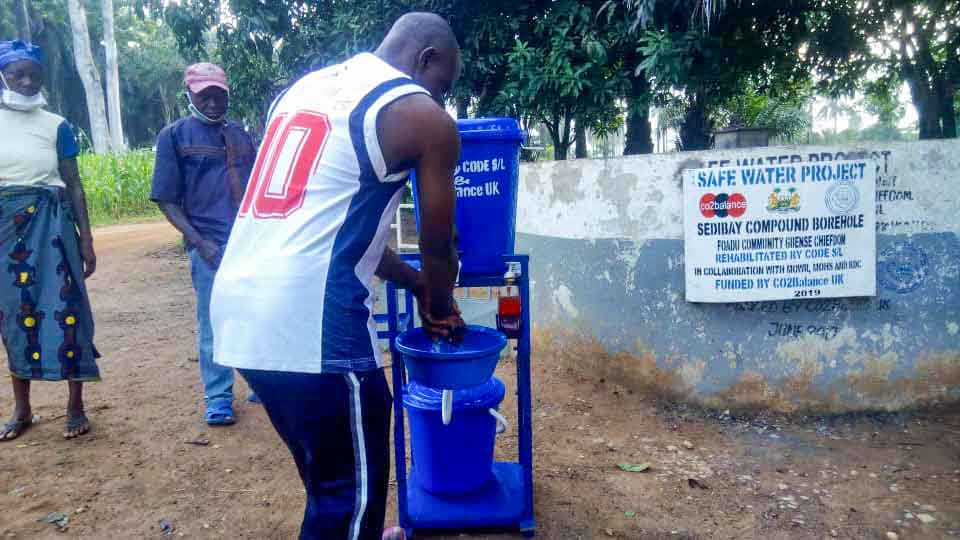
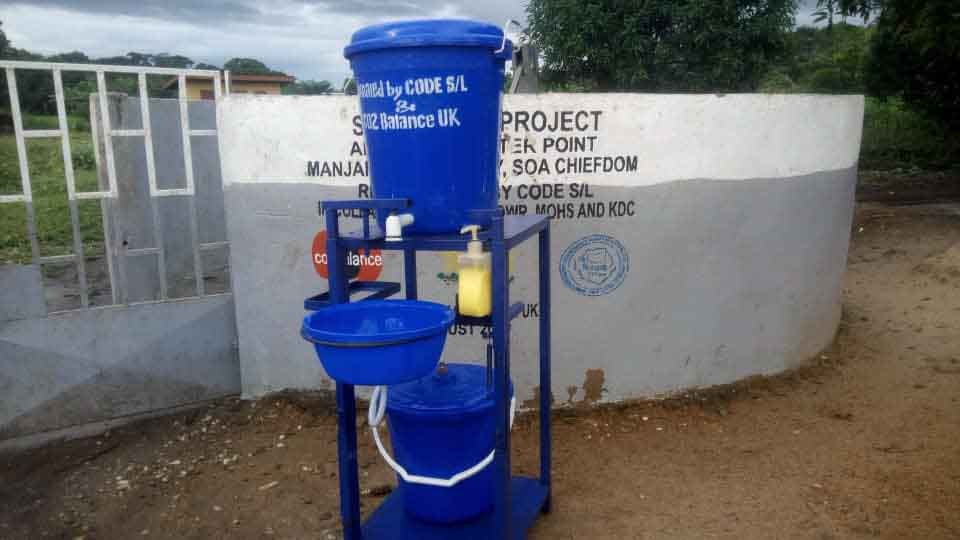
Our project is helping communities in the Kono region to restore 57 wells. In cooperation with the local population, damaged wells are repaired and regularly maintained, which secures the regional water supply. The availability of clean drinking water eliminates the need to boil water, saving CO2 emissions.
Thus, it not only contributes to climate action but also impacts gender equality. Girls and women are particularly affected by poor water conditions due to the responsibility of household water supply. Providing clean water through boreholes reduces their time spent collecting water and firewood, which can now be used for education or additional income.

According to UNICEF, 2.2 billion people worldwide lack reliable access to safe and clean drinking water – 26% of the global population. Women and girls often must travel long distances to collect water from the nearest water point. To make the water safe for use, it is typically boiled over open fires using wood, which generates carbon emissions and harmful smoke. Additionally, the collection of firewood contributes to deforestation.
Climate projects for clean drinking water offer practical solutions. Water can be treated chemically (e.g., with chlorine-based purifiers), mechanically (e.g., with water filters), or through tapping groundwater from wells. For this, wells must be repaired, maintained, or newly installed, as only functioning wells provide clean drinking water. These solutions grant even remote villages access to safe water.
Such projects also reduce carbon emissions by eliminating the need to boil water and help combat deforestation. The clean drinking water projects in ClimatePartner's portfolio are registered with international standards.
Four criteria for projects to meet quality thresholds
The life cycle of a climate project
A climate project has a set life cycle consisting of various phases, from the feasibility assessment to the retirement of Verified Emission Reductions (VERs).The project developer reviews the general feasibility of the project, the project design, and the financing. Then, the Project Design Document (PDD) is prepared, which contains all the basic information about the project, such as the objective, location, timeline, and duration.
In this phase, independent auditors examine the PDD and the information it contains. This phase often also involves field visits with on-side interviews and analyses. Auditors are accredited, impartial assessors who have to be approved by the relevant standard as a validation and verification body (VVB). TÜV Nord/Süd, S&A Carbon LLC., and SCS Global Services are examples of VVBs."
Once validated, the project can be registered with a standard such as the Verified Carbon Standard or the Gold Standard. All high-quality climate projects are based on international standards. They provide the framework for project design, construction, carbon accounting, and monitoring. Recognised standards make the climate project system and the projects themselves resilient, traceable, and credible.
After the climate project has been registered, the monitoring begins. Here, the project developers monitor and document the data of the project activities and progress. The duration of the monitoring phase varies from project to project: it can cover two years, but documentation over five or seven years is also possible.
At the end of each monitoring phase, a VVB checks and assesses whether the values and project activities stated in the monitoring report are correct. As with validation, visits to the project site are often part of the verification process.
Once verified, the emission reductions that were confirmed in the verification phase can be issued as VERs. The steps of monitoring, verification, and issuance of VERs are repeated regularly and are therefore considered as a cycle.
Once a VER has been used, it must be retired. This process is also reflected in the registry. If the financing of a climate project is done through ClimatePartner, the VERs are bundled in a system certified by TÜV Austria and then retired on a regular basis. This ensures that each VER can no longer be sold and is only used once, preventing double counting.
Explore our projects
Biochar for Climate Action, Healthy Soils, and Better Harvests

A certified climate project combined with additional commitment
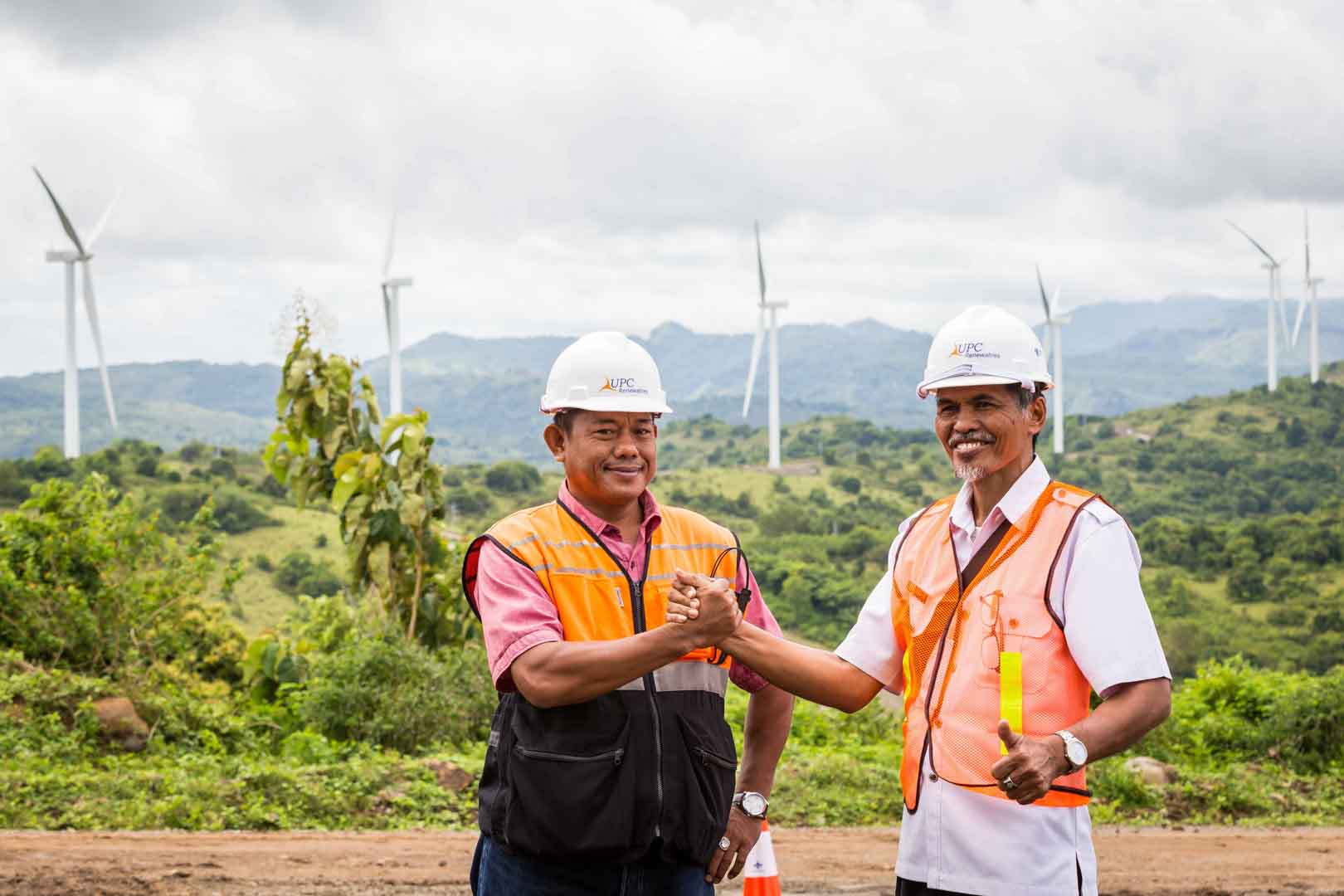

Expansion of renewable energy generation in Asia
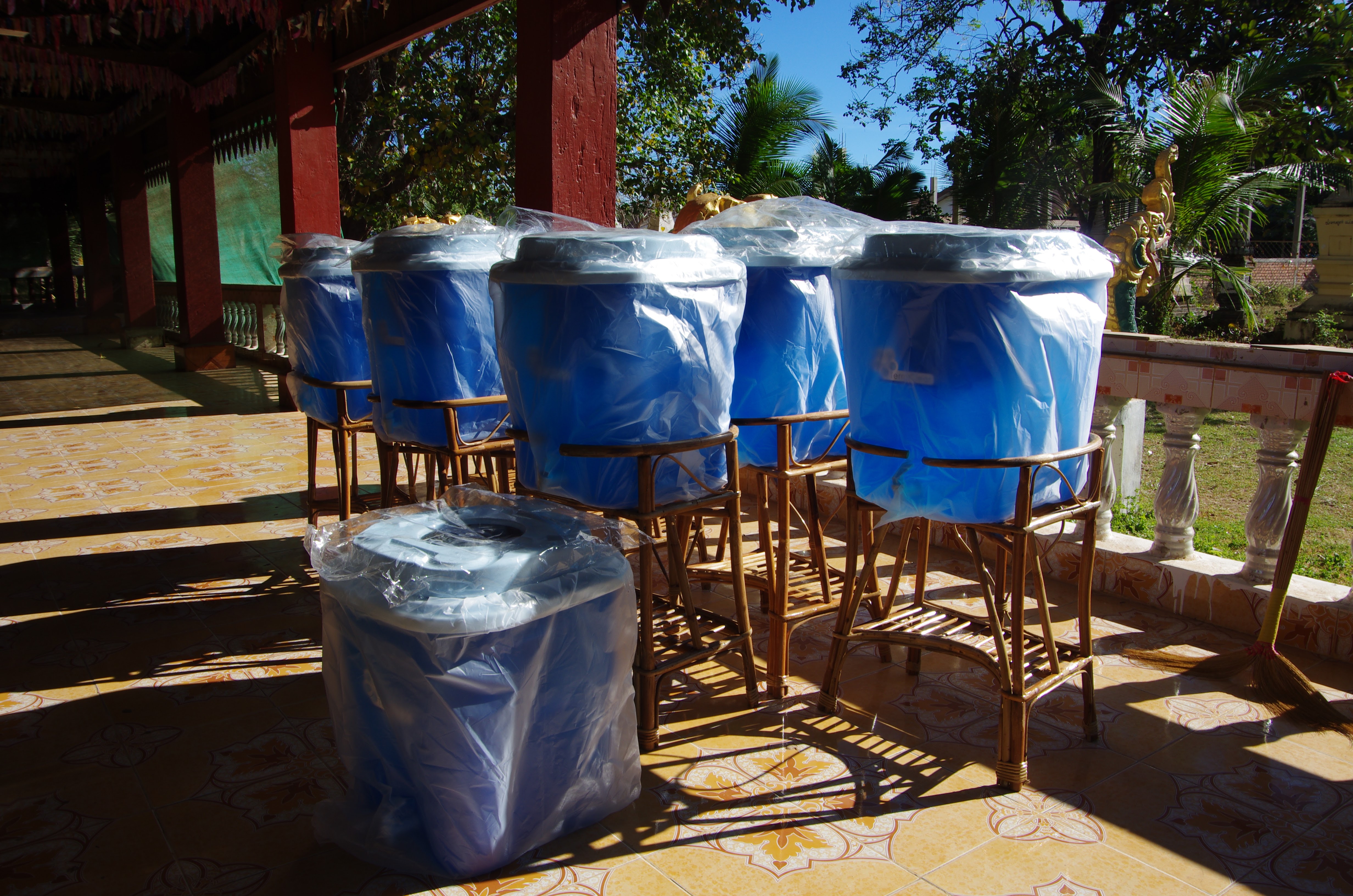

Ceramic water filters save CO2 and improve health
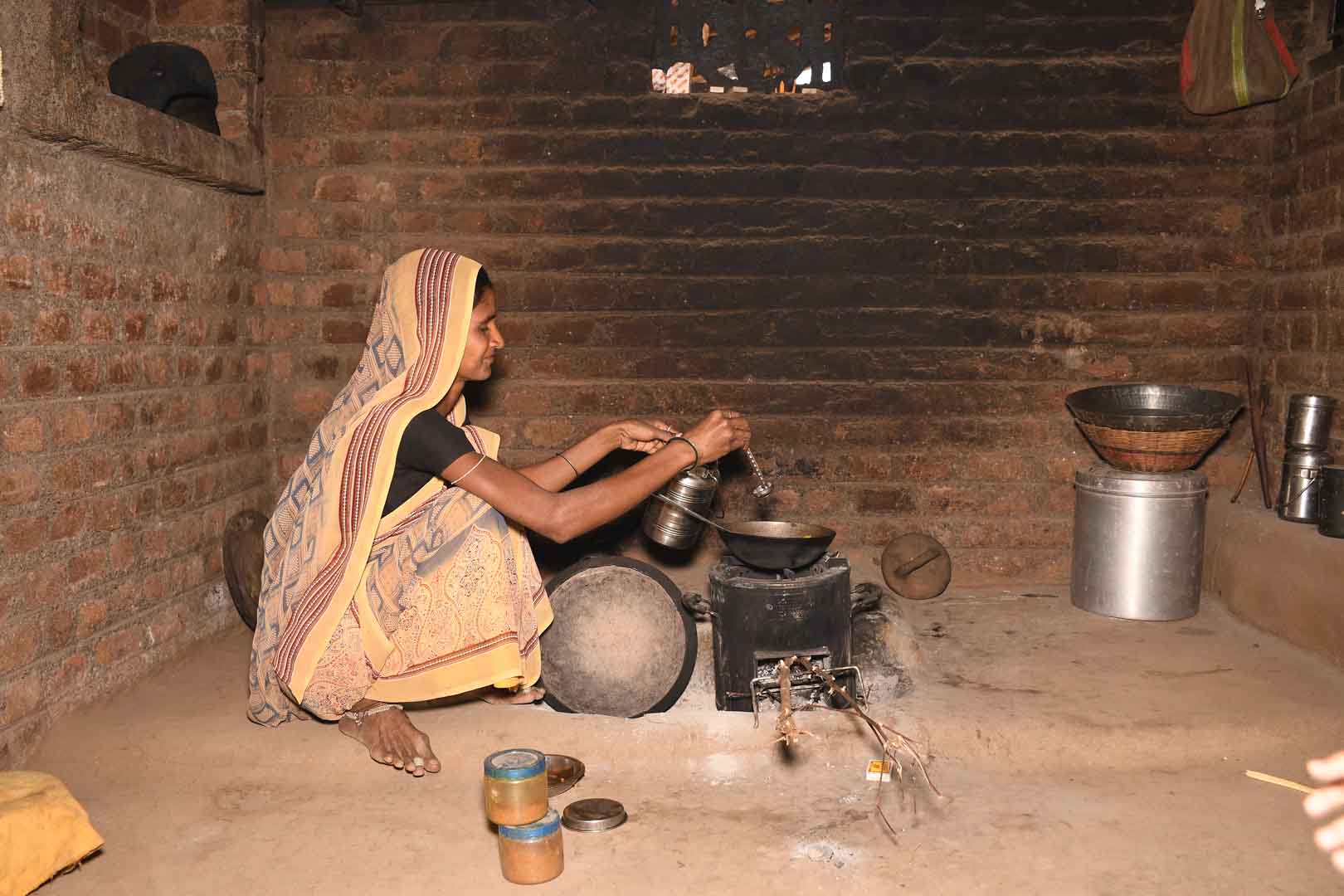

Improved cookstoves worldwide – for better health and cleaner air

A certified climate project combined with additional commitment
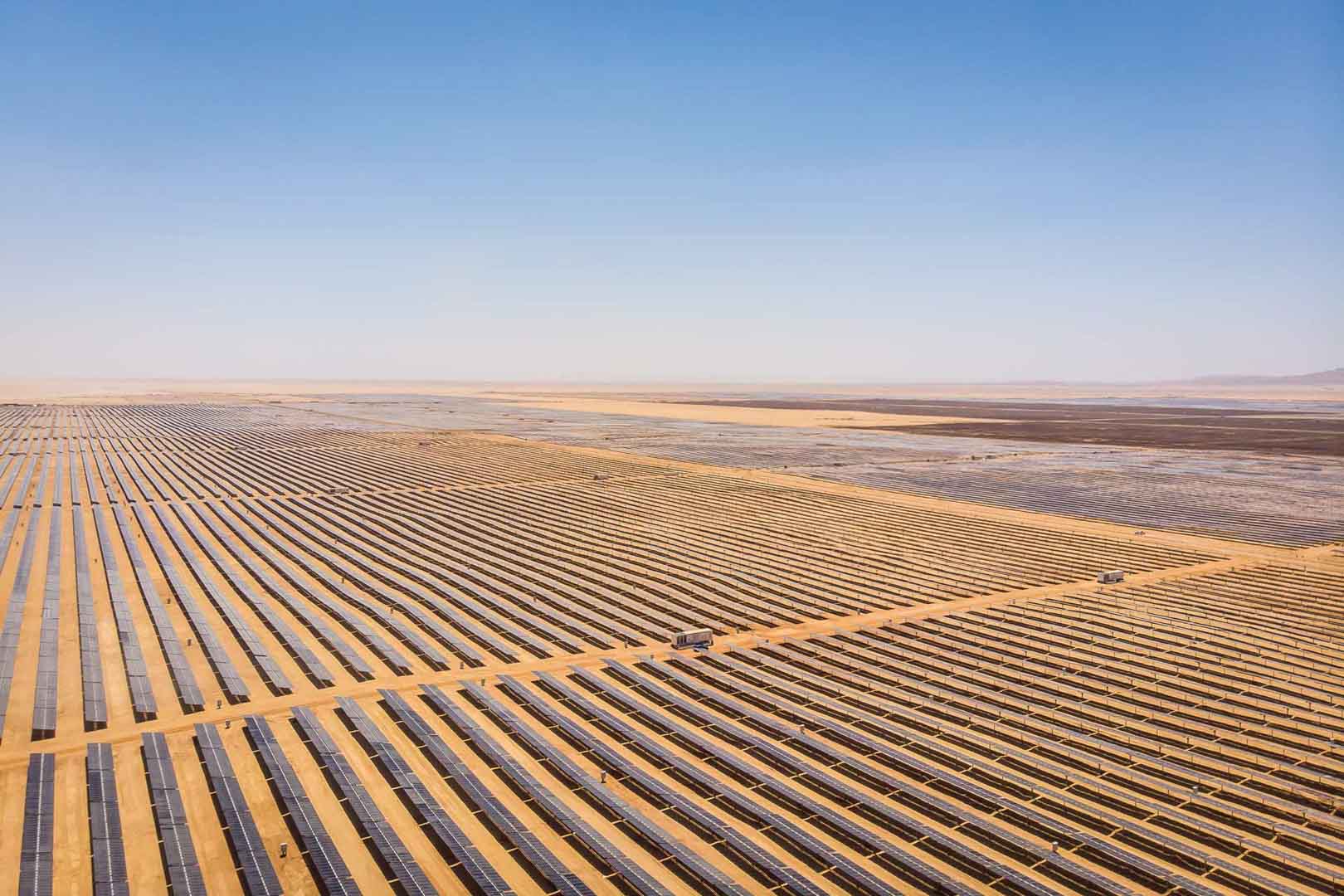

Powering access to renewable energy in Africa
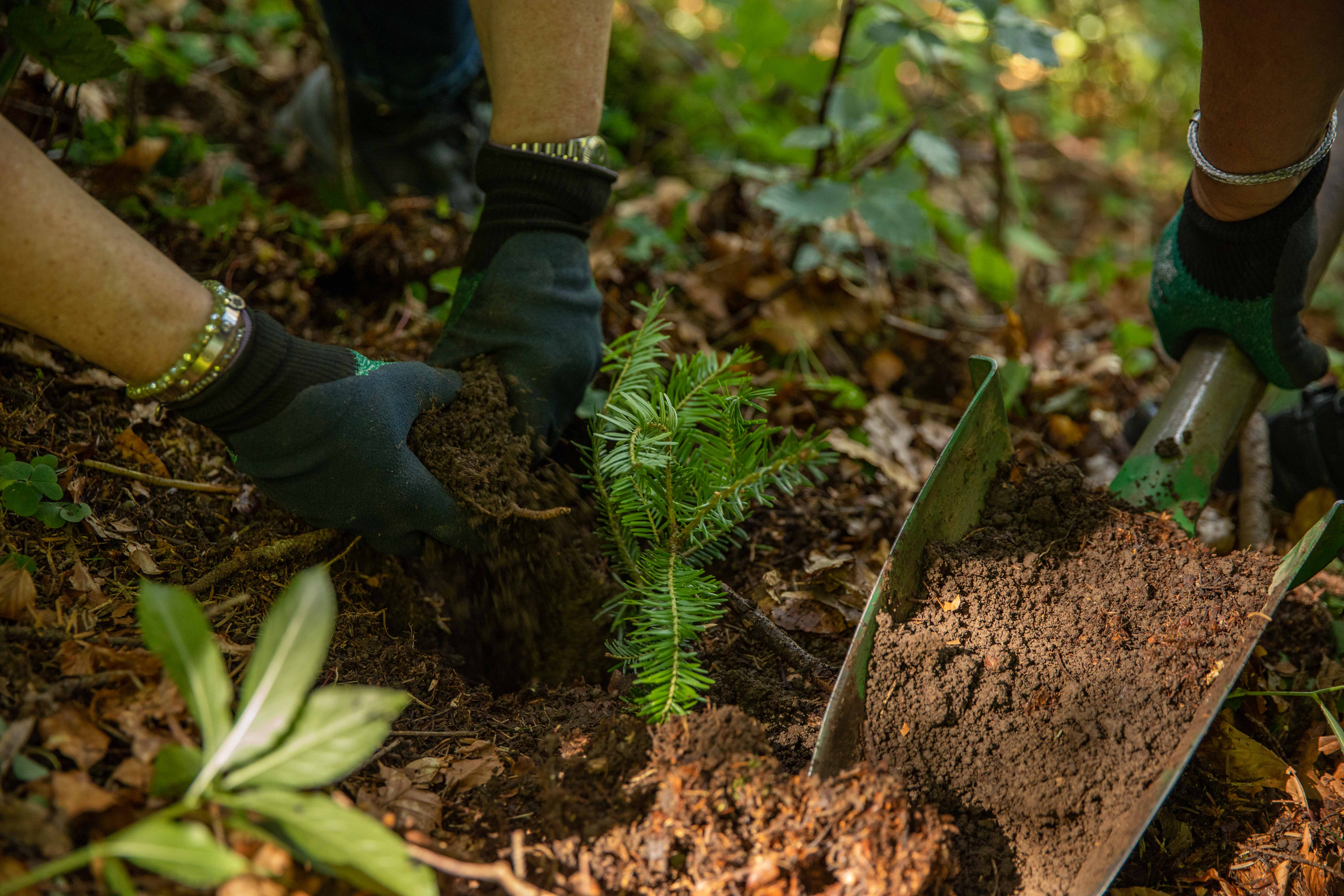

A certified climate project combined with additional commitment

Restored ecosystems remove carbon
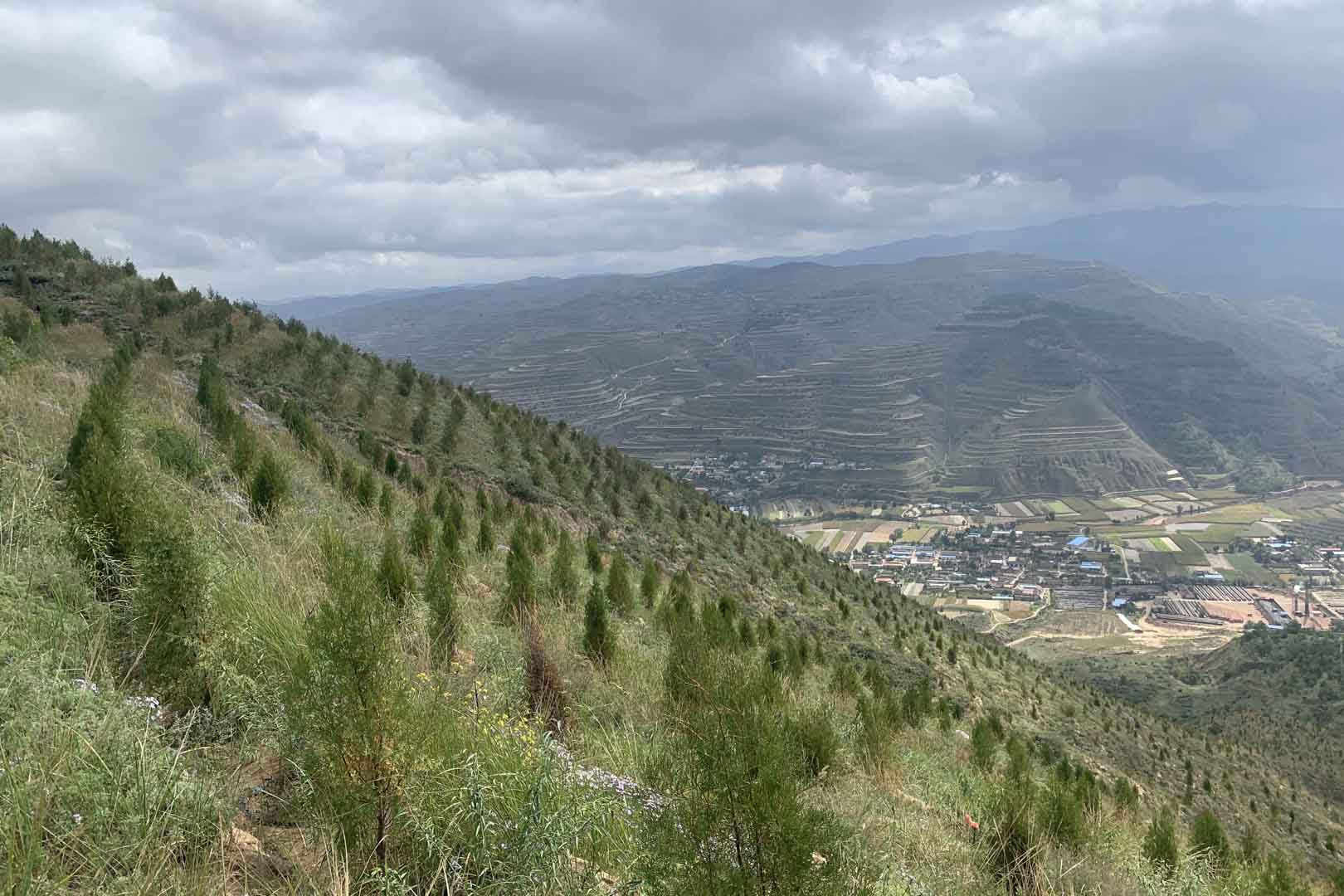

Turning degraded farmlands into healthy ecosystems
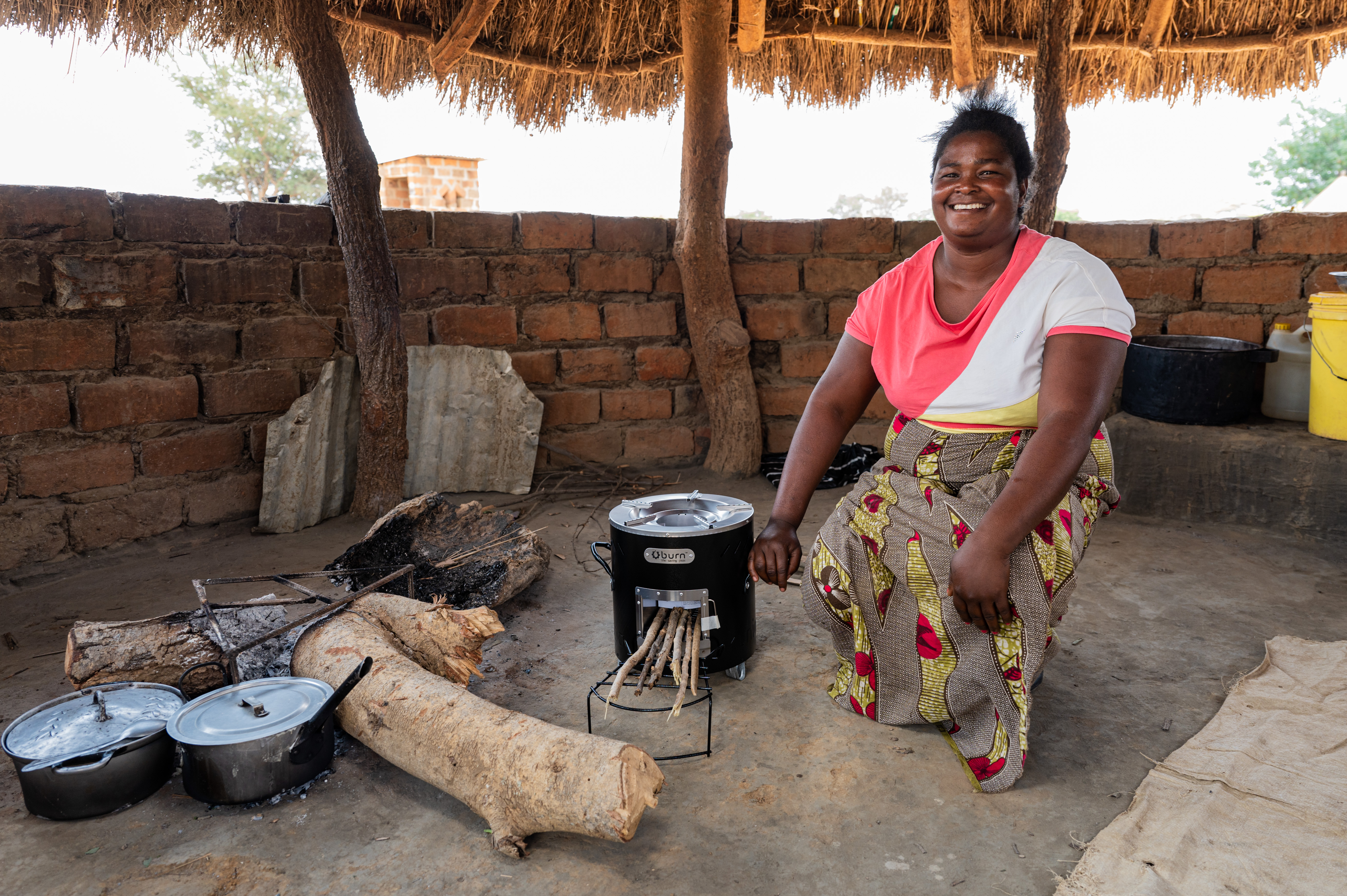

Improved cookstoves - better for health and the environment